Plants and animals are made up of millions of cells and these cells have several similarities and differences.
Considering that they are both eukaryotic cells, which means they have a true nucleus, that is enclosed and separated from other organelles by a nuclear membrane, is a crucial factor that defines their modes of multiplication. They have similar reproduction processes of mitosis and meiosis, using their DNA that is housed by the cell nucleus.
Interesting Science Videos
What are plant cells and animal cells?
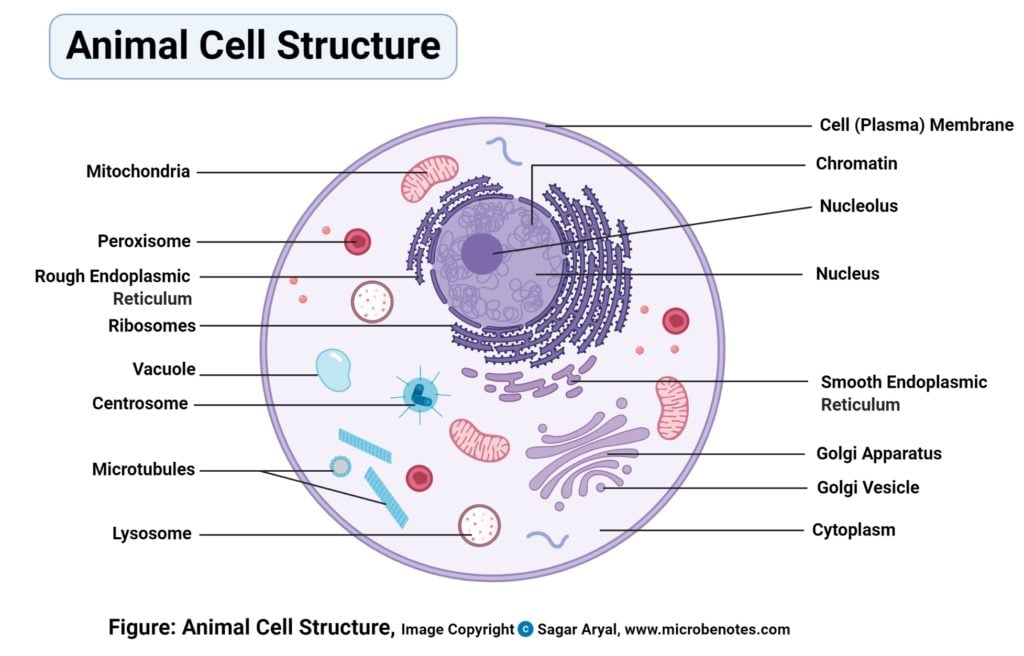
They are also both membrane-bound, with several cell organelles in common performing the same if not similar mechanisms to maintain and control the cells’ normal function. These organelles include the nucleus, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, cytoskeleton, peroxisomes, and the cell membrane.
They also undergo cellular respiration, which performs processes of energy production used to grow the cell and maintain its normal functions.
Despite having all these similarities they have several differences as well.
Structurally, plant and animal cells are very similar because they are both eukaryotic cells. They both contain membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes. Both also contain similar membranes, cytosol, and cytoskeletal elements. The functions of these organelles are extremely similar between the two classes of cells (peroxisomes perform additional complex functions in plant cells having to do with cellular respiration). However, the few differences that exist between plants and animals are very significant and reflect a difference in the functions of each cell.
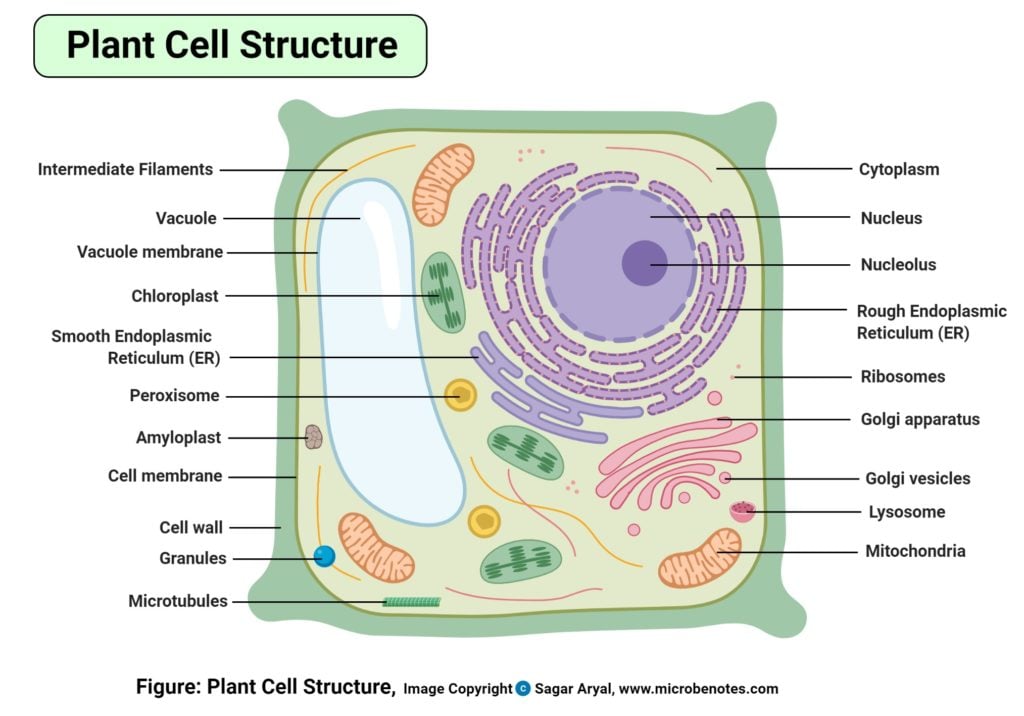
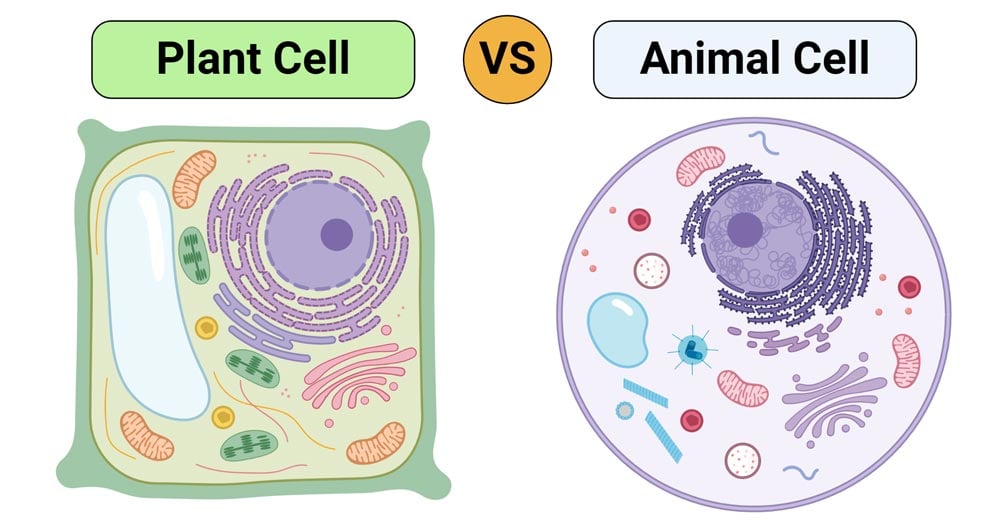
Plant cells can be larger than animal cells. The normal range for an animal cell varies from 10 to 30 micrometers while that for a plant cell stretches from 10 to 100 micrometers. Beyond size, the main structural differences between plant and animal cells lie in a few additional structures found in plant cells. These structures include chloroplasts, the cell wall, and vacuoles.
Animal cell vs. Plant cell (Table form)
| Characteristic | Animal cell | Plant cell |
| Definition | Animal cells are also the basic functional unit of life for animals constituting all cell organelles that perform a variety of functions to support the animals’ metabolisms. | Plant cells are basic functional units of plants constituting all cell organelles performing a variety of functions that support the plants’ metabolisms. |
| Size and shape | Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells with their cells ranging from 10-30um in length. Animal cell shapes and sizes vary greatly from irregular shapes to round shapes, most defined by the function they perform. | Plant cells are larger than animal cells with the cell size ranging from 10um-100um in length. Plant cells are similar in shape with most cells being rectangular or cube-shaped. |
| Cell wall | They lack the cell wall but possess a plasma (cell) membrane, which performs the function of support and protection of the cell from external damage. It also plays a major role in selective permeability allowing in and outflow of nutrient molecules, water, and other cell elements. | They have both a cell wall that is made up of cell membrane and cellulose. The cell wall is, a rigid membrane matrix found on the surface of all plant cells whose primary role is to protect the cell and its content. |
| Plasma membrane | They have a plasma membrane that is a thin flexible membrane, which acts as a protective covering for the animal cell. It also has selective permeability. | The presence of the plasma membrane made up of cellulose, just below the cell wall allows selective permeability of cell contents into and out of the cell cytoplasm. |
| Cytoplasm | It houses all the cell organelles. | It houses most of the cell organelles |
| Ribosomes | They are present and are used for protein synthesis and genetic coding of the protein, amino acid sequences. | They are present and are used for protein synthesis and cellular repair mechanisms. |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | They are present in two types: rough endoplasmic and smooth endoplasmic reticulum | They are present, in two types; rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
| Lysosomes | Animal cells have lysosomes, that contain digestive enzymes to break down cellular macromolecules. | Plant cells rarely contain lysosomes as the plant vacuole and the Golgi bodies handle molecule degradation of waste cellular products. |
| Vacuoles | Animal cells may have many small vacuoles, a lot smaller than the plant cell. | Plant cells have a large central vacuole that can occupy up to 90% of the cell’s volume. |
| Nucleus | Present and it lies at the center of the cell | Present and it lies on the side of the cell |
| Nucleolus | Present in the nucleus | Present in the nucleus |
| Centrioles | They are present with their major function involving the assistance of the cell division process. | They are absent in plant cells |
| Peroxisomes | They are present in the cytoplasm. They perform the oxidation mechanisms for specific biomolecules and they assist in the synthesis of plasmalogen lipids. | They are present in the cell cytoplasm functioning as cell oxidizers for cellular molecules, synthesis of lipids, and recycling carbon from phosphoglycolate during photorespiration. |
| Microfilaments and microtubules | They are present functioning to give support to the cell cytoskeleton, transport materials across the cytoplasm into and out of the nucleus. They are also involved d in cytokinesis. | They are present, to give cytoskeletal support, transportation of molecules across the cytoplasm and the nucleus and they play a major role in cytokinesis. |
| Cytoskeletons | Present and its major functions include creating a network that organizes the cell components and maintains the cell shape. | They have a cytoskeleton that maintains the plant cell shape, supports the cell cytoplasm and maintains the cell’s structural organization. |
| Cytosol | Present and its where all the cell organelles are suspended | Present, it’s where most of the cell organelles are suspended. |
| Microvilli | They are present in the intestinal lining to increase the surface area for the absorption of food. | Absent in plant cells. |
| Granules | Present | Present |
| Cilia and Filaments | Present; they allow movement of cells or part of the cell, for example, swimming of the sperm to the ova. | Absent in plants |
| Plastids | Absent | Present; they give pigmentation color to the plants and also facilitate trapping of light energy used for photosynthesis. |
| Plasmodesmata | Absent | Present; they facilitate the communication and transport of materials across plant cells. |
| Golgi bodies | They have larger and fewer Golgi bodies with their major function being to process and package protein and lipid macromolecules as they are being synthesized. | They have smaller but more Golgi bodies with their major role being a modification, processing, sorting, and packaging proteins for cellular secretion. |
| Synthesis of cellular nutrients | They cannot synthesize amino acids, vitamins, and coenzymes. | They can synthesize amino acids, vitamins, and vitamins. |
| Cytokinesis | It takes place by constriction | It takes place in the cell plates |
| Osmosis in a hypotonic solution | They take in water molecules by osmosis and easily burst when placed in hypotonic solution because of the lack of a cell wall | They absorb water molecules by osmosis but they do not burst in a hypotonic solution due to the presence of a cell wall. |
References and Sources
- 3% – https://www.bioexplorer.net/difference-between-plant-and-animal-cells.html/
- 2% – https://brainly.com/question/11566088
- 2% – https://answersdrive.com/what-is-the-difference-between-plant-and-animal-cells-7203906
- 2% – https://answersdrive.com/what-are-the-similarities-between-animal-and-plant-cells-7292357
- 1% – https://www.thoughtco.com/what-is-a-plant-cell-373384
- 1% – https://www.thoughtco.com/vacuole-organelle-373617
- 1% – https://www.thoughtco.com/differences-between-mitosis-and-meiosis-373390
- 1% – https://www.thoughtco.com/animal-cells-vs-plant-cells-373375
- 1% – https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-pits-and-plasmodesmata/
- 1% – https://biologywise.com/plant-cell-structure-function
- 1% – https://biologydictionary.net/osmosis/
- <1% – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AcrqIxt8am8
- <1% – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_Th0bsASzmM
- <1% – https://nrcca.cals.cornell.edu/soilFertilityCA/CA1/CA1_print.html
- <1% – https://biologywise.com/smooth-endoplasmic-reticulum-function
- <1% – https://biologywise.com/plant-cell-vs-animal-cell
- <1% – https://biologywise.com/plant-cell-organelles
- <1% – https://biodifferences.com/difference-between-plant-cell-and-animal-cell.html
- <1% – https://answersdrive.com/what-is-the-difference-between-the-plasma-membrane-and-the-cell-membrane-1493230
- <1% – http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_nucleus.html

thank you
This information was very helpful, thank you.
nice information
this helped so much
very good thanks for the help
Pretty good
thank you very much
it’s very helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for the reply ,i applicate.
Thanks
It helps alot 👍i really like👊 it i will share it to my friends.
Thank you so much for liking our websites and also thanks for sharing with your friends.
Wow thanks dude gnarly stuff dude
This helped me with my studies and I am so thankful, thank you so very much that you have made this site I really want to become a teacher i have one more year until I can do that and this will be thought to my kids.
wow….I have lean more about cell, thanks
This is very good summary, it will help a lot
Yes it really helps alot .
Thank you very much sir is really helpful
So helpful. I like it 👍
Congratulation
Thanks for explaining to us, it really help me in my assignment
What do they mean by the animal cell cytoplasm houses “most” of the organelles? What does the animal cell house that the plant cell doesn’t in the cytoplasm?
Thanks for that great work
Definitely helps especially if you’re learning about cells and you just need more information before your test.
this is a very nice article
it is not
I need a Diagram For Both The Plants And Animals Cell
It’s there na
What are the plant cell
The cells in the plants.
Nice
Very Very good
Very nice article and will help everyone. I will share this to my friends. Thanks