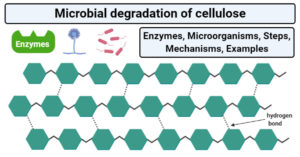
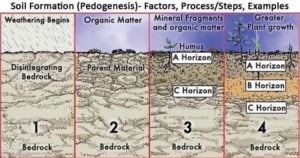
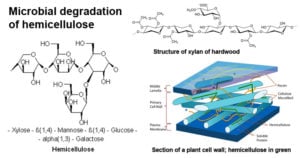
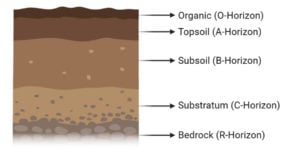
Microorganisms found in soil with effects and examples
Soil microbiology is a branch of soil science concerned with soil-inhabiting microorganisms, their functions, and activities within the soil ecosystem. Read Also: Soil Formation (Pedogenesis)- Factors, Process/Steps, Examples Microorganisms found in … Read more