Malaria (Plasmodium): A-Level Biology Revision Notes
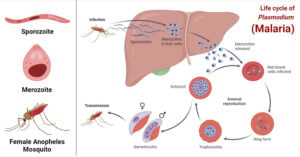
Malaria is an infectious disease that is caused by one of five species of protozoa Plasmodium. Plasmodium is an unicellular obligate parasite that infects the red blood cells, liver and … Read more