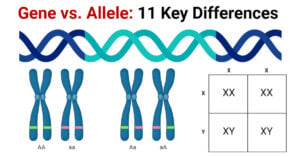
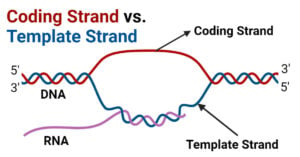
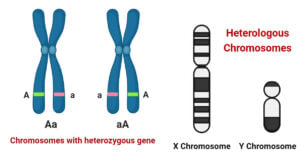
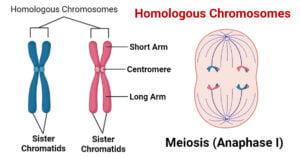
Gene vs. Allele: Definition and 11 Key Differences
DNA, deoxyribose nucleic acid, is present in the cell’s nucleus. DNA, a gene containing chromosomes, passes from parents to offspring. It binds around the histone protein, which gets condensed and … Read more