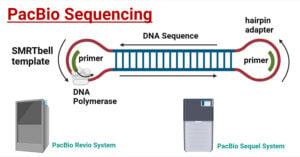
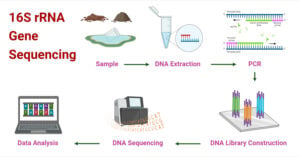
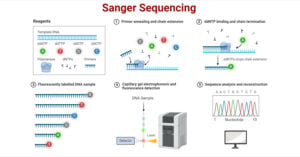
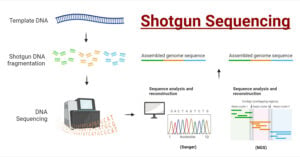
PacBio Sequencing: Principle, Steps, Types, Applications
PacBio sequencing, also known as Single Molecule Real-Time (SMRT) DNA Sequencing, is a type of third-generation sequencing method developed by Pacific Biosciences that allows the real-time observation of DNA synthesis … Read more