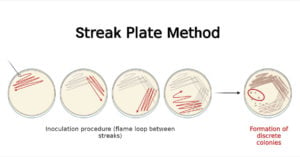
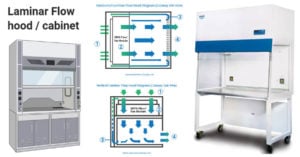
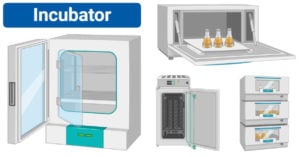
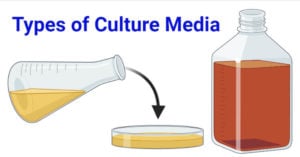
Microbiology: History, Branches, Career Opportunities
Microbiology is the branch of science that studies microorganisms which include a diverse group of simple microscopic living organisms including bacteria, viruses, fungi, archaea, and protozoa. This field of study … Read more