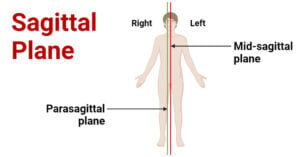
Sagittal Plane: Definition, Regions, Movement, Applications
The movement of our body occurs in three different anatomical planes of motion: coronal, sagittal, and transverse. The three planes of the body can be briefly discussed below: Coronal (frontal … Read more