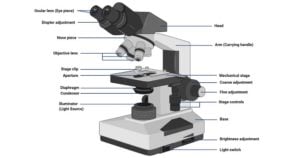
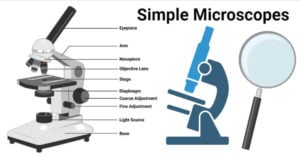
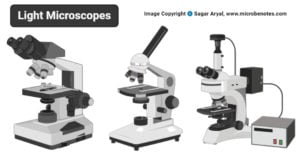
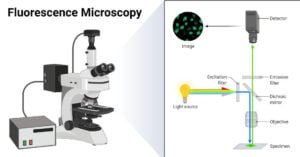
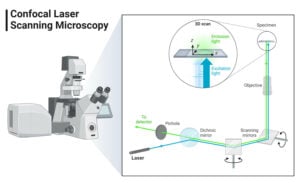
Parts of a microscope with functions and labeled diagram
Having been constructed in the 16th Century, microscopes have revolutionized science with their ability to magnify small objects such as microbial cells, producing images with definitive structures that are identifiable … Read more