Interesting Science Videos
Peroxisomes Definition
- Peroxisomes are small, membrane-enclosed cellular organelles containing oxidative enzymes that are involved in a variety of metabolic reactions, including several aspects of energy metabolism.
- They are considered as an important type of microbody found in both plants and animal cells.
- They were identified as organelles by Belgian cytologist Christian de Duve in 1967 after already been described.
- First peroxisomes to be discovered were isolated from leaf homogenate of spinach.
- They are most abundantly found in detoxifying organs such as the liver and kidney cells. However, they can be induced to proliferate in response to metabolic needs.
Structure of Peroxisomes
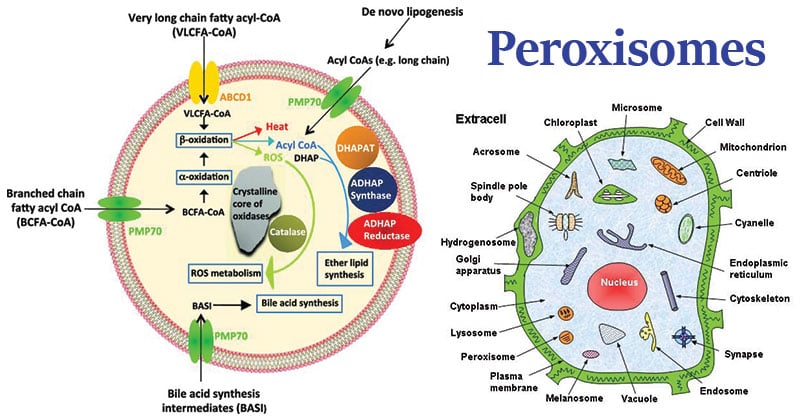
Figure: Diagram of Peroxisomes. Image Source: Irfan J Lodhi (DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.01.002)
- They are membrane-bound spherical bodies of 0.2 to 1.5 μm in diameter found in all eukaryotic organisms including both plants and animal cells.
- They are found floating freely in the cytoplasm in close association of ER, mitochondria or chloroplast within the cell.
- They are among the simplest of eukaryotic organelles.
- They exist either in the form of a network of interconnected tubules called peroxisome reticulum or as individual microperoxisomes.
- They are variable in size and shape according to the cell and usually circular in cross-section.
- They range from 0.2 -1.5 μm in diameter.
- It consists of a single limiting membrane of lipid and protein molecules enclosing the granular matrix.
- The matrix consists of fibrils or a crystalloid structure containing enzymes.
Peroxisomal Enzymes
- Approximately 60 known enzymes are present in the matrix of peroxisomes.
- They are responsible to carry out oxidation reactions leading to the production of hydrogen peroxide.
- The main groups of enzymes include:
- Urate oxidase
- D-amino acid oxidase
- Catalase
Functions of Peroxisomes
- Hydrogen Peroxide Metabolism:
- Enzymes present in the peroxisomes both lead to the production and elimination of H202 which is a reactive oxygen species.
- Fatty acid oxidation:
- Oxidation of fatty acids, in animal cells, occurs in both peroxisomes and mitochondria, but in yeasts and plants, only limited to peroxisomes.
- Oxidation is accompanied by the production of H202 which is decomposed by catalase enzyme. This provides a major source of metabolic energy.
- Lipid biosynthesis
- Synthesis of cholesterol and dolichol occurs in both ER and peroxisomes. Bile acid synthesis takes place from cholesterol in the liver.
- Peroxisomes contain enzymes to synthesize plasmalogens, a family of phospholipids which are important membrane components of tissues of the heart and brain.
- Germination of seeds
- Peroxisomes in seeds responsible for the conversion of stored fatty acids to carbohydrates, critical to providing energy and raw materials for the growth of germinating plants.
- Photorespiration
- Peroxisomes in leaves particularly in the green ones carry out the photorespiration process along with chloroplasts.
- Degradation of purines
- Carry out the catabolism of purines, polyamines and amino acids especially by uric acid oxidase
- Bioluminescence
- Luciferase enzyme found in the peroxisomes of fireflies help in bioluminescence and thus aid the flies in finding a mate or its meal.
References
- Verma, P. S., & Agrawal, V. K. (2006). Cell Biology, Genetics, Molecular Biology, Evolution & Ecology (1 ed.). S .Chand and company Ltd.
- Alberts, B. (2004). Essential cell biology. New York, NY: Garland Science Pub.
- Kar,D.K. and halder,S. (2015). Cell biology genetics and molecular biology.kolkata, New central book agency
- R and suwal,S.N. (2010).Human Anatomy and physiology. Kathmandu, vidyarthi prakashan (p.) ltd.
- https://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/peroxisomes/peroxisomes.html
- https://www.britannica.com/science/peroxisome
- http://www.biologydiscussion.com/cell/difference-and-similarity-between-lysosomes-and-peroxisomes-biology/1834
- http://study.com/academy/lesson/peroxisomes-definition-structurefunctions.html#courseInfo

Well explained and easy to comprehend.
Very good
Hello
Dr. sagar aryal. I am a student at Umm Al-Qura University in Saudi Arabia. My doctor asked me to do research on Peroxisome. And I ask your permission to take some information and put your source on it
Hi Ahmad,
Sure, you can use the information from our website with citation to our website.