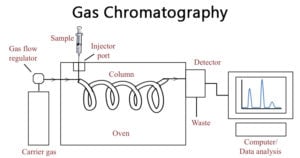
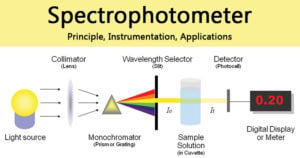
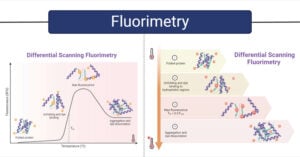
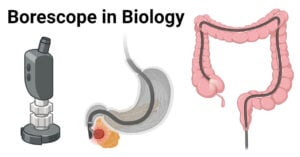
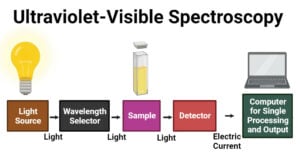
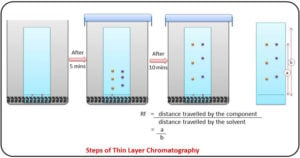
Gas Chromatography: Principle, Parts, Steps, Procedure, Uses
Gas chromatography differs from other forms of chromatography in that the mobile phase is a gas and the components are separated as vapors. Image Source: Bitesize Bio. Principle of Gas … Read more