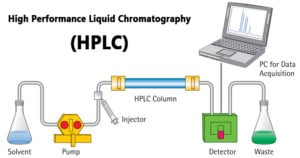
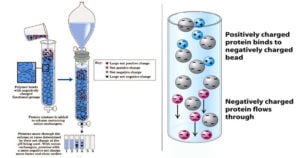
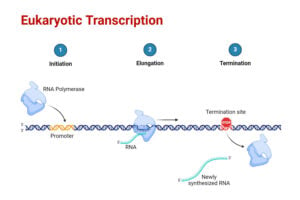
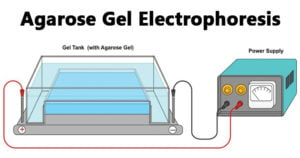
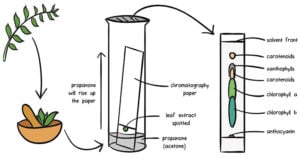
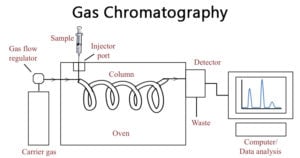
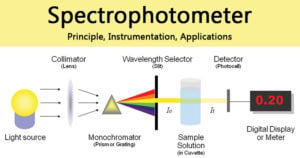
HPLC: Principle, Parts, Types, Uses, Diagram
High-performance liquid chromatography or commonly known as HPLC, is an analytical technique used to separate, identify or quantify each component in a mixture. The mixture is separated using the basic … Read more