| S.N. | Character | Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
| 1. | Term Origin | Greek for “primitive nucleus” | Greek for “true nucleus” |
| 2. | Definition | Organisms are made up of cell(s) that lack a cell nucleus or any membrane-encased organelles. | Organisms are made up of cells that possess a membrane-bound nucleus as well as membrane-bound organelles. |
| 3. | Major groups | Bacteria, Archae, and Bluegreen algae | Algae, fungi, protozoa, plants, animals |
| 4. | Origin | Around 3.5 billion years ago. | Around 2 billion years ago. |
| 5. | Size (approximate) | 0.5-3.0 μm | >5 μm |
| 6. | Cell Type | Usually unicellular (some cyanobacteria may be multicellular) | Usually multicellular |
| 7. | Complexity | Simple | Complex organization. |
| 8. | Nucleus Location | Free in the cytoplasm, attached to mesosomes | Contained in membrane-bound structure |
| 9. | Nuclear membrane | No nuclear membrane. | Classic membrane present. |
| 10. | Nucleolus | Absent | Present |
| 11. | Chromosome number | One | More than one |
| 12. | Chromosome shape | Circular | Linear |
| 13. | Genes | Expressed in groups called operons. | Expressed individually |
| 14. | Genome | DNA haploid genome | DNA diploid genome |
| 15. | DNA base ratio (G+C %) | 28-73 | About 40 |
| 16. | DNA wrapping on proteins | Multiple proteins act together to fold and condense prokaryotic DNA. Folded DNA is then organized into a variety of conformations that are supercoiled and wound around tetramers of the HU protein. | Eukaryotes wrap their DNA around proteins called histones. |
| 17. | Genome nature | Efficient and compact with little repetitive DNA. | With large amounts of non-coding repetitive DNA. |
| 18. | Membrane-bound organelles | Absent | Present |
| 19. | Ribosomes (sedimentation coefficient) | 70S (50S + 30S).Smaller. | 80S (60S + 40S). Larger. |
| 20. | Ribosome’s location | Free in the cytoplasm or bound to the cell membrane | Attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum |
| 21. | Mitochondria | Absent | Present |
| 22. | Golgi bodies | Absent | Present |
| 23. | Endoplasmic reticulum | Absent | Present |
| 24. | Mesosomes | Present. Performs the function of Golgi bodies and mitochondria and also helps in the separation of the chromosome during cell division. | Absent |
| 25. | Lysosomes | Absent | Present |
| 26. | Peroxisomes | Absent | Present |
| 27. | Chloroplasts | Absent; chlorophyll scattered in the cytoplasm | Present (in plants) |
| 28. | Fimbriae | Prokaryotes may have pili and fimbriae (appendage that can be found on many Gram-negative and some Gram-positive bacteria). | Absent |
| 29. | Microtubules | Absent or rare | Present |
| 30. | Centrosome | Absent | Present except in flowering plants. |
| 31. | Cytoskeleton | May be absent | Present |
| 32. | Glycocalyx | Present | Only in some |
| 33. | Cytoplasmic streaming | Absent | Present |
| 34. | Cytoplasmic membrane | Does not contain sterols (except Mycoplasma) | Contains sterols |
| 35. | Cell wall | Complex structure containing protein, lipids, and peptidoglycans | Present for plant cells and fungi; otherwise absent |
| 36. | Muramic acid | Present | Absent |
| 37. | Movement | Simple flagellum, if present | Complex flagellum, if present |
| 38. | Respiration | Via cytoplasmic membrane | Via mitochondria |
| 39. | Energy production site | Electron transport chain located in the cell membrane | Within membrane-bound mitochondria |
| 40. | Metabolic rate | Higher due to larger surface area to volume ratio | Comparatively slow |
| 41. | Reproduction | Asexual (binary fission) | Sexual and asexual/ Mitotic division |
| 42. | Generation time | Shorter | Comparatively longer |
| 43. | Genetic Recombination | Partial, unidirectional transfer | Meiosis and fusion of gametes |
| 44. | Zygote | Merozygotic (partially diploid) | Diploid |
| 45. | Extrachromosomal DNA | Plasmid | Inside the mitochondria |
| 46. | DNA replication | Occurs in the cytoplasm. | Occurs in the nucleus. |
| 47. | Transcription and translation | Occurs simultaneously. | Transcription occurs in the nucleus and then translation occurs in the cytoplasm. |
Interesting Science Videos
Prokaryotes Definition
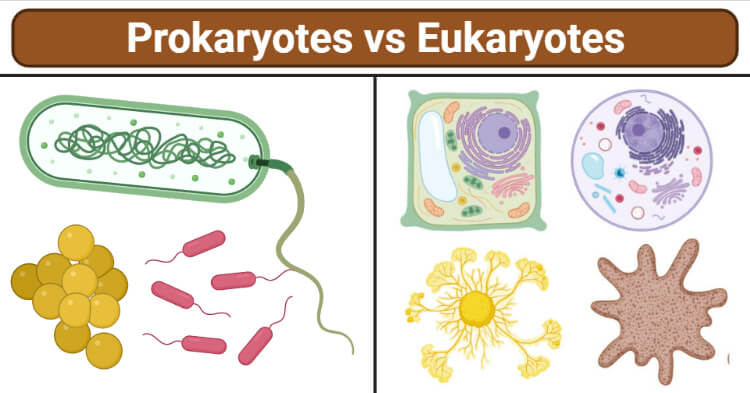
Prokaryotes are single-celled entities that are primitive in structure and function as they lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles. The term “prokaryote” is derived from two Greek words, ‘pro’ meaning ‘before’ and ‘karyon’ meaning ‘nucleus’. Prokaryotes are considered to be the first living organisms of the earth as they are the simplest form of life.
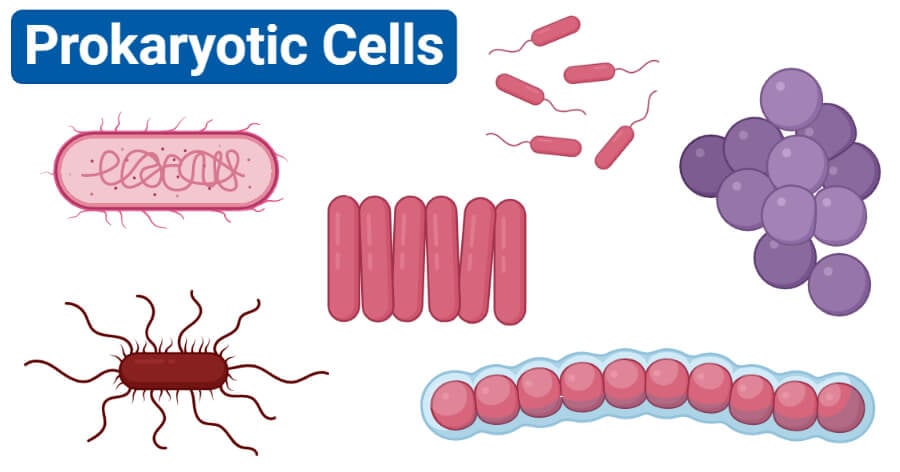
Image created using biorender.com
Characteristics of Prokaryotes
The general characteristics of prokaryotic cells are listed below:
- In general, Prokaryotes range in size from 0.1 to 5.0 µm and are considerably smaller than eukaryotic cells.
- The shape of Prokaryotes ranges from cocci, bacilli, spirilla, and vibrio. However, prokaryotic cells with modifications of these shapes are also found in nature.
- The cellular organization of prokaryotic cells is primitive as they lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound cell organelles.
- The genetic material of prokaryotic cells in a single chromosome is made up of a single strand of DNA.
- A critical protein, histone protein, that is found bound in the chromosomes of eukaryotes is absent in prokaryotic cells.
- Prokaryotic cells also lack the nucleolus and the mitotic apparatus.
- The cell wall of prokaryotic cells is non-cellulosic and is made up of carbohydrates and lipids.
- Prokaryotic cells are asexual and thus, reproduce via asexual means without the formation of gametes.
Prokaryotes Structure (Components/ Parts)
The structure of a prokaryote is not as complex as eukaryotic cells as they have primitive cell organelles. Generally, most prokaryotic cells have the following components/ parts:
- This is an additional outer covering in some prokaryotic cells that serve to protect the cell against foreign invaders.
- The capsule is made up of polysaccharides, that allows the cells to cling to various surfaces and preserves the moisture in the cell.
- The cell wall is a tough coring of prokaryotic cells present inside the capsule.
- The cell wall of most prokaryotes is made up of polymer of carbohydrates and lipids termed, peptidoglycan.
- In Archaeal cells, however, the cell wall doesn’t contain peptidoglycan but some other structure called pseudopeptidoglycan. It Is made up of proteins and other polymers.
- The cell wall provides shape to the cell while protecting the cell organelles present in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- Underneath the cell wall is a cell membrane that is made up of phospholipid.
- The phospholipid forms a bilayer consisting of lipid composed of glycerol attached to a hydrophobic phosphate head and two hydrophilic fatty acid tails.
- In archaea, the phospholipid tails are usually connected, forming a monolayer instead of the bilayer structure.
- The plasma membrane in prokaryotic cells provides protection to the cell while allowing the transport of essential molecules in and out of the cell.
- The cytoplasm is the entire space of cells present inside of the cell membrane.
- It contains a gel-like cytosol and water-based solution that contains minerals and other ions essential for the cell.
- Besides, the cytoplasm also contains other cellular structures like the chromosomes and ribosomes.
- All prokaryotic cells have 70S ribosomes. The 70S ribosomes are made up of two subunits, 30S, and 50S.
- Here, the 50S subunit contains 23S, and 5S rRNA and the 30S subunit contains 16S rRNA.
- The ribosome is the most commonly observed internal structure in prokaryotic cells.
- The size and number of ribosomes differ in different prokaryotic cells.
- The ribosome is responsible for the formation of polypeptides and in turn, proteins.
- Nucleoid region
- The nucleoid region of cytoplasm in prokaryotic cells contains a single circular chromosome and small rings of extrachromosomal DNA called plasmids.
- The single circular chromosome is present as a single copy of genetic material in contrast to the two copies of DNA in eukaryotes.
- The prokaryotic genomes are also smaller in size than the eukaryotic genomes.
- The plasmids, in turn, are copied independently copied outside of the chromosomes. These plasmids might carry some non-essential genes.
- Appendages
- Many prokaryotic cells have cell appendages that protrude out from the cell surface as flagella, pili, and fimbriae.
- Flagella are the most common appendages in many prokaryotic cells.
- These are tail-like structures that assist the cell in moving around.
- Fimbriae are thin filamentous structures that are used to stick the cells to various surfaces.
- Pilli, in turn, are longer filaments that have different roles in different cells. One example of this is the sex pilli that holds two cells together as they transfer the DNA molecules by the process of conjugation.
Division of Prokaryotes (Reproduction)
As mentioned earlier, prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually without the formation of gametes. Some asexual modes of reproduction in prokaryotes are:
Binary fission
- Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction where a single living cell or an organelle grows twice its size and then splits into two identical daughter cells, where each of these daughter cells has the potential to grow into the size of the original cell or organelle.
- Binary fission is the mode of reproduction in many prokaryotes including, archaea, cyanobacteria, and eubacteria.
- During this process, the genetic material of the parent cell is equally divided into two daughter cells. As a result, no genetic variation is observed in the newly formed prokaryotic cells.
Steps of binary fission
- The DNA of the cell divides to form two identical DNA molecules, both of which are moved towards the cell membrane.
- The cell then doubles its size, and the cell membrane slowly starts to divide with each having a copy of the DNA.
- Once the division of the cell membrane is completed, the cell wall is formed between the two strands of DNA dividing the parent cell into two identical daughter cells.
Recombination
- Another asexual mode of reproduction in prokaryotic cells is via recombination.
- In this case, the genetic material of one cell is incorporated into the cell of another prokaryote via transduction, transformation, and conjugation.
- In conjugation, two cells are connected via sex pilli where genes are transferred through the pilli.
- In transformation, the prokaryotic cell takes up the genetic material from the environment and incorporates it into the bacterial chromosome.
- In transduction, the exchange of genes occurs via viral infection. The bacteriophage first infects one bacterium and takes up the targeted gene and transfers it to another cell.
Prokaryotes Examples
Bacterial cells
- Bacteria are the single-celled organisms that are found in all ecosystems throughout the world.
- The cell wall of the bacterial cell is formed of peptidoglycan that makes it tough and thick.
- Capsules are unique to some bacteria and thus might not be present in other prokaryotic cells.
- The genetic material of bacteria is present in the form of circular coils of chromosomes.
- Examples of bacterial cells are E. coli, Streptomyces spp, Pseudomonas spp, etc.
Archaeal cell (Archaea)
- Archaeal cells are similar to bacterial cells as they too are primitive unicellular organisms.
- Archaeal cells are mostly found in extreme environments like hot springs, oceans, and marshlands.
- The capsule is not present in archaeal cells, and the cell wall is made up of pseudopeptidoglycan, composed of proteins.
- Similarly, the cell membrane of archaeal cells has a monolayer of phospholipid that protects the cell against harsh environments.
- Examples of archaeal cells are Halobacterium spp, Thermoplasma spp, Sulfolobus spp, etc.
FAQs on Prokaryotes
What are three examples of Prokaryotes?
Any three examples of Prokaryotes are blue-green algae, E. coli, and mycoplasma.
Do Prokaryotes have ribosomes?
Yes, Prokaryotes have ribosomes. The ribosome is of 70S type.
Do Prokaryotes have a nucleus?
No, Prokaryotes do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, but they do have a nucleoid region in the cytoplasm that contains the genetic material.
Do Prokaryotes have mitochondria?
No, Prokaryotes do not have mitochondria.
Is DNA found in Prokaryotes?
Yes, DNA is found as genetic material and extrachromosomal plastids in Prokaryotes.
How do Prokaryotes divide?
Prokaryotes divide through asexual methods like binary fission and conjugation.
Eukaryotes Definition
Eukaryotes are cells that are complex in structure and function as they have a membrane-bound well-defined nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
- The term “eukaryote” is derived from Greek words, “eu” meaning ‘true’ and “karyon’ meaning ‘nucleus.’
- Eukaryotic cells have a more advanced structural composition when compared to prokaryotes.
- By virtue of these advancements, eukaryotic cells are capable of performing more complex functions than prokaryotic cells.
Characteristics of Eukaryotes
The general characteristics of eukaryotic cells are listed below:
- The size of Eukaryotes is significantly larger than prokaryotic cells as the size ranges from 10-100 µm in diameter.
- The shape of Eukaryotes varies significantly with the type of cell. Some cells are pleiomorphic like Amoeba, whereas some have a defined shape like plant cells. The shape of the cells is highly influenced by environmental factors as well as other functional adaptations.
- Eukaryotic cells have a more advanced cellular organization with multiple membrane-bound organelles and well-defined nucleus.
- The genetic material of Eukaryotes is DNA, and it is linear and has multiple origins of replication.
- The nucleus of eukaryotic cells is surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. The chromosomes in the nucleus are complexed with histone protein to form linear chromosomes as opposed to circular chromosomes of prokaryotes.
- The cell wall that is present in some Eukaryotes is made up of cellulose or other carbohydrates.
- Some eukaryotic cells like yeast cells reproduce asexually via mitosis or fission, whereas other cells reproduce sexually.
Eukaryotes Structure (components/ parts)
Eukaryotes are much larger in size when compared with prokaryotic cells, having a volume about 10,000 times higher than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are formed of a number of membrane-bound and membrane-less organelles that all perform together to support the cell’s organization and function. The common component/ parts in eukaryotic cells are as follows:
Cell wall
- The cell wall is present in some eukaryotic cells like some protists, fungal and plant cells.
- The cell wall in plants and some protists is made up of cellulose microfibrils and a network of glycans embedded in the matrix of pectin polysaccharides.
- The composition of the cell wall in fungal cells is different as in fungal cells, the cell wall is composed of a different polysaccharide, chitin.
- The function of the cell wall, however, is similar in eukaryotic cells. The cell wall provides support and shape to the eukaryotic cells.
Cell membrane/ Plasma membrane/ Cytoplasmic membrane
- The cell membrane in eukaryotic cells is present inside the cell wall.
- In cells without the cell wall, the cell membrane functions as the outermost covering that separates the internal contents of the cell from the outside environment.
- The plasma membrane is made up of phospholipid bilayer with integral proteins embedded between the two layers.
- The composition of the cell membrane is similar in eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Cytoplasm
- The cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell is a fluid-filled space that accommodates all internal cell organelles and other molecules.
- The cytoplasm consists of a jelly-like cytosol and a water-soluble solution containing minerals, ions and other molecules.
- The amount of cytoplasm is higher in eukaryotic cells as compared to prokaryotic cells as the cell volume is more abundant in eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus
- The nucleus is an organelle present in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell.
- It is more complicated than the prokaryotic nucleus as the nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane having a composition similar to the plasma membrane.
- The genome of a eukaryotic cell is present inside the nucleus where it remains coupled with various proteins like the histone protein.
- Inside the nucleus, the DNA molecules are arranged in chromosomes which are linear and more organized.
- Additionally, the nucleus also houses a nucleolus that is not surrounded by a membrane but has proteins that make up the ribosomes and rRNA.
Ribosomes
- In eukaryotic cells, the ribosomes are 80S type containing 60S and 40S subunits.
- The larger subunit is further composed of 5S RNA, 28S RNA, and proteins, whereas the smaller subunit is composed of 18S RNA and 33 proteins.
- The ribosomes in eukaryotic cells are found either attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or are found free in the cytoplasm.
Mitochondria and Plastids
- Mitochondria and plastids are membrane-bound organelles found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.
- Both mitochondria and plastids have an extrachromosomal DNA that regulates the functions of the organelles.
- In mitochondria, the outer membrane is made up of phospholipid bilayer, whereas the inner layer is folded into cristae where the major physiological function of the cell takes place.
- Plastids are found in eukaryotic cells of plants and algae that provide color to the cell. Additionally, plastids also have a green pigment, chlorophyll, which is required for photosynthesis.
Cytoskeletal structures
- Many eukaryotic cells have cytoplasmic projections like flagella and cilia that are involved in movement, feeding, and sensation of these cells.
- These structures are mainly composed of tubulin proteins supported by microfilaments and microtubules.
- Cytoskeletal structures are also present in the cytoplasm that provides shape and support to the cell.
Division of Eukaryotes (Reproduction)
Some eukaryotic cells can divide only by asexual means while other eukaryotic cells divide both sexually as well as asexually.
Asexual reproduction
- Asexual reproduction is common in all eukaryotic cells except for reproductive cells that form the male and female gamete.
- The most common mode of asexual reproduction is mitosis, where the cell grows double its size and then divided to form two identical daughter cells.
- Unicellular fungal cells and protists divide by budding where new cells arise on the surface of dividing cells in the form of a chain.
- Processes like binary fission and multiple fission are also observed in cells of primitive eukaryotes.
- Some fungi are also known to divide/ reproduce asexually via sporulation.
Sexual reproduction
- The cells of the reproductive system in plants and animals are divided by the sexual method.
- In this method, the cell divided meiotically to form four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes to their parent cell.
- The sexual reproduction in eukaryotic cells is responsible for the variation in different cells.
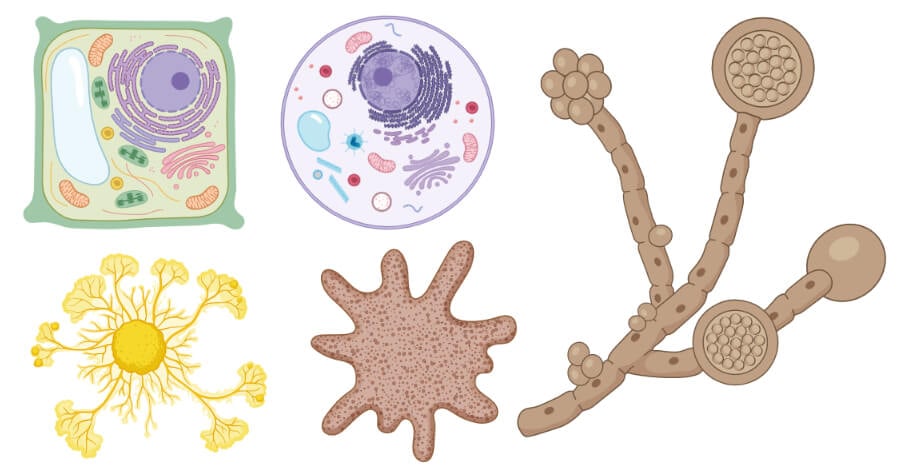
Eukaryotes Examples
Plant cell
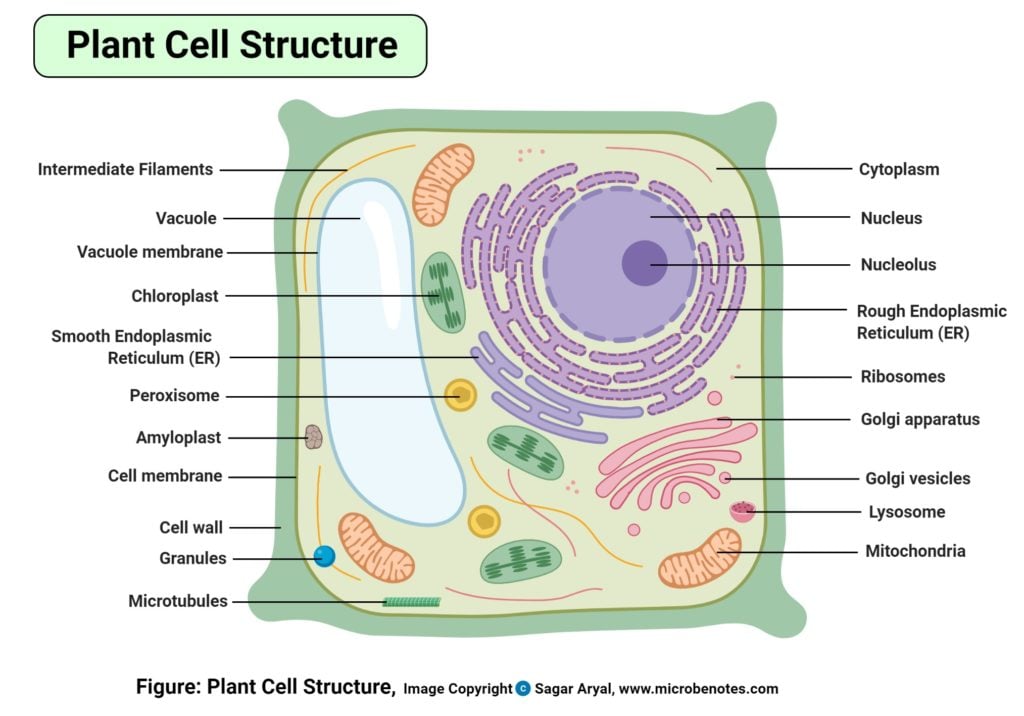
- Plant cells are examples of Eukaryotes where there is a thick cell wall made up of cellulose that provides the shape and structure to the cell.
- Each plant cell has a larger vacuole in the cytoplasm that maintains the turgor pressure of the cell.
- Additionally, plant cells are unique among eukaryotic cells as they have chloroplasts containing chlorophyll that plays an essential role during the process of photosynthesis.
Animal cell
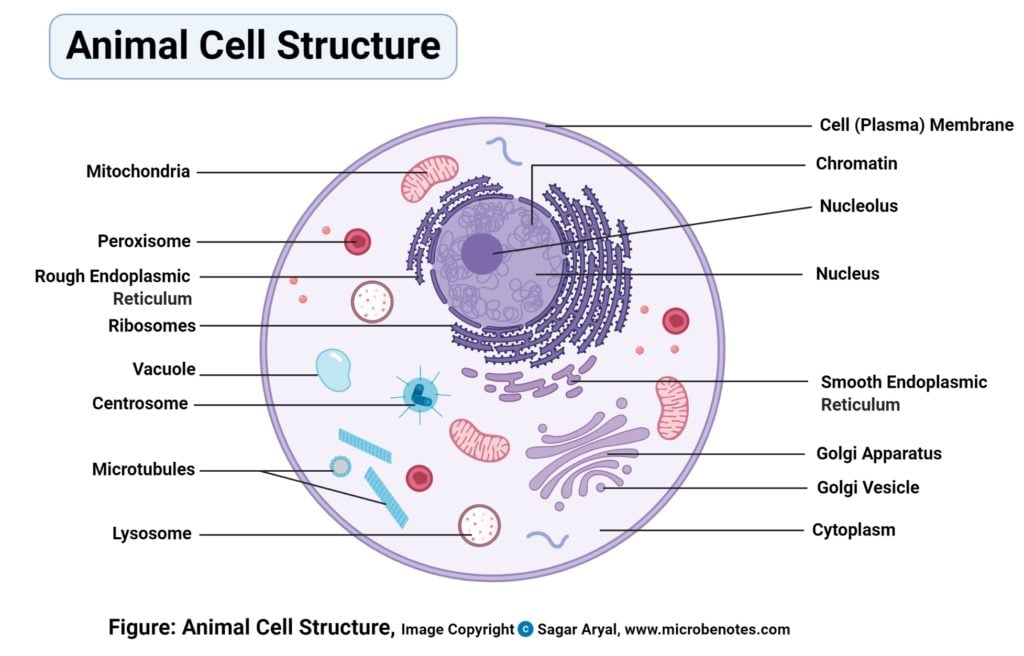
- Animal cells are another group of Eukaryotes that do not have a rigid cell wall.
- The lack of cell wall in animals allows the cells to acquire different shapes and assists the process of phagocytosis and pinocytosis.
- Animal cells are different from plant cells as they have a smaller vacuole, and they don’t have chloroplasts.
- Animal cells have additional organelles, centriole, that generates the mitotic apparatus required during cell division.
Fungal cells
- Fungal cells are similar to plant cells in that they also have a rigid cell wall.
- However, the cell wall is made up of chitin and not cellulose.
- Some fungi are unicellular like yeasts, which have tiny holes in their cell membrane that allows the cells to exchange cytoplasm and other organelles.
Protists
- Protists are the unicellular eukaryotes that are primitive when compared to plant or animal cells.
- Most protists don’t have a cell wall while some might.
- Many protists are known to have chloroplast containing chlorophyll while others might have other photosynthetic pigments.
- Protists are known to have cilia and flagella that assist in the movement of the cells.
References
- Cooper GM. The Cell: A Molecular Approach. 2nd edition. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2000. The Origin and Evolution of Cells. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9841/.
- Murray, Patrick R. (2016). Medical Microbiology.Eighth edition. India: Elsevier Inc.
- Parija S.C. (2012). Textbook of Microbiology & Immunology.(2 ed.). India: Elsevier India.
- Lane N. Energetics and genetics across the prokaryote-eukaryote divide. Biol Direct. 2011;6:35. Published 2011 Jun 30. doi:10.1186/1745-6150-6-35.
- Tellez G. Prokaryotes Versus Eukaryotes: Who is Hosting Whom?. Front Vet Sci. 2014;1:3. Published 2014 Oct 14. doi:10.3389/fvets.2014.00003.
- Vellai T, Vida G. The origin of eukaryotes: the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Proc Biol Sci. 1999;266(1428):1571-1577. doi:10.1098/rspb.1999.0817.
- Mariscal C, Doolittle WF. Eukaryotes first: how could that be?. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015;370(1678):20140322. doi:10.1098/rstb.2014.0322.
- Murat D, Byrne M, Komeili A. Cell biology of prokaryotic organelles. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2(10):a000422. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a000422.
- Theriot JA. Why are bacteria different from eukaryotes?. BMC Biol. 2013;11:119. Published 2013 Dec 13. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-11-119.
- Nilkanta C, Bagchi A. Comparative analysis of prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription factors using machine-learning techniques. Bioinformation. 2018;14(6):315-326. Published 2018 Jun 30. doi:10.6026/97320630014315.
- Sapp J. The prokaryote-eukaryote dichotomy: meanings and mythology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005;69(2):292-305. doi:10.1128/MMBR.69.2.292-305.2005.
- Whitman WB, Coleman DC, Wiebe WJ. Prokaryotes: the unseen majority. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(12):6578-6583. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.12.6578.
- Margolin W, Bernander R. How do prokaryotic cells cycle?. Curr Biol. 2004;14(18):R768-R770. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2004.09.017.
- Nanninga N. Cytokinesis in prokaryotes and eukaryotes: common principles and different solutions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2001;65(2):319-333. doi:10.1128/MMBR.65.2.319-333.2001.
- Cridge AG, Major LL, Mahagaonkar AA, Poole ES, Isaksson LA, Tate WP. Comparison of characteristics and function of translation termination signals between and within prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(7):1959-1973. Published 2006 Apr 13. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl074.
- Brocchieri L, Karlin S. Protein length in eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(10):3390-3400. Published 2005 Jun 10. doi:10.1093/nar/gki615.
- Poole AM, Phillips MJ, Penny D. Prokaryote and eukaryote evolvability. Biosystems. 2003 May;69(2-3):163-85. doi: 10.1016/s0303-2647(02)00131-4. PMID: 12689728.
- https://www.livescience.com/65922-prokaryotic-vs-eukaryotic-cells.html
- https://www.technologynetworks.com/cell-science/articles/prokaryotes-vs-eukaryotes-what-are-the-key-differences-336095
- https://www.visiblebody.com/learn/biology/cells/prokaryotes-vs-eukaryotes
- https://www.thoughtco.com/what-are-prokaryotes-and-eukaryotes-129478
- https://biologydictionary.net/prokaryotes-vs-eukaryotes/
- https://www.diffen.com/difference/Eukaryotic_Cell_vs_Prokaryotic_Cell
- https://science.howstuffworks.com/life/cellular-microscopic/prokaryotic-vs-eukaryotic-cells.htm
- https://tutors.com/lesson/prokaryotic-vs-eukaryotic-cells
- https://rsscience.com/eukaryote-prokaryote/
- https://www.nku.edu/~whitsonma/Bio150LSite/Lab%205%20Cells/Bio150LRCellTypes.htm
- https://thisonevsthatone.com/prokaryotes-vs-eukaryotes/
- https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/2.2/primary/lesson/prokaryotic-and-eukaryotic-cells-bio/
- https://askabiologist.asu.edu/prokaryotes-vs-eukaryotes
- https://ib.bioninja.com.au/standard-level/topic-1-cell-biology/12-ultrastructure-of-cells/prokaryotic-versus-eukaryot.html
- https://sciencing.com/prokaryotic-vs-eukaryotic-cells-similarities-differences-13717689.html
- https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-wmopen-biology1/chapter/prokaryotes-and-eukaryotes/
- https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/what-is-the-difference-between-prokaryotic-and-eukaryotic-cells-1523518350-1
- https://www.sciencefacts.net/prokaryotes-vs-eukaryotes.html
- https://www.sciencenewsforstudents.org/article/explainer-prokaryotes-and-eukaryotes
- https://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/Eukaryotic-and-Prokaryotic-Cells-Similarities-and-Differences.aspx
- https://sciencetrends.com/prokaryotes-vs-eukaryotes-whats-the-difference/
- https://pediaa.com/difference-between-prokaryotes-and-eukaryotes/
- https://www.azolifesciences.com/article/Eukaryotic-vs-Prokaryotic-Cells.aspx
- https://www.microscopemaster.com/prokaryotes.html

bur some of the pages are not fully seen especali tabled and charts
Very good notes. As a first year student I really loved your notes. May Almighty bless you Amen.
Your effort in putting this up is commendable. Well done
This information is really understandable hence readable. As a first year student doing BSc I really love your notes. Keep the good work up and God bless your work Amen.
Thank you so much
Great effort …
I reaLLy LIke The effoRt DeaR
Thanks a lot . A great effort. Thumbs up.