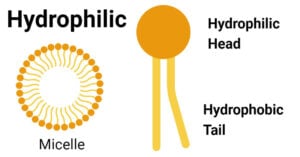
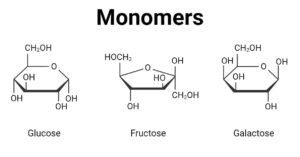
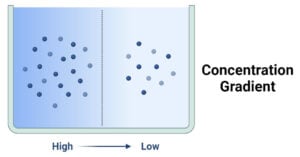
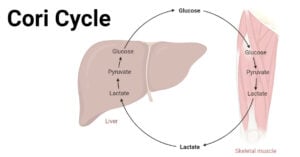
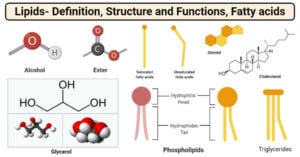
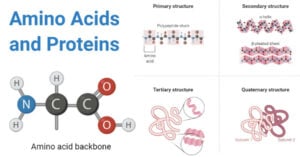
Hydrophilic Molecule: Definition, Examples, Applications
The term hydrophilic means “water-loving”. The two divided parts of the hydrophilic prefix “hydro” means water, and the suffix “philic” means loving. A hydrophilic molecule is a water-soluble molecule that … Read more