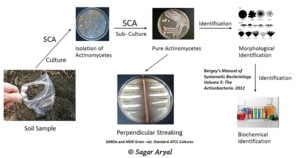
Pour Plate Method- Definition, Principle, Procedure, Uses
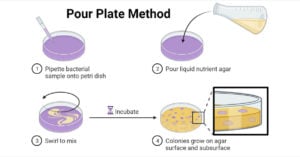
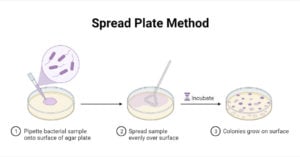
The pour Plate Method technique was established in the laboratory of Robert Koch and is still being used widely since his period. This method is suitable for facultative, Microaerophilic, and … Read more