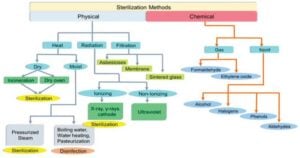
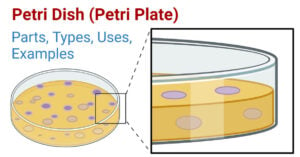
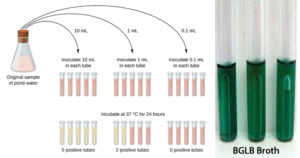
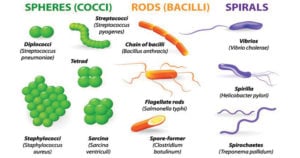
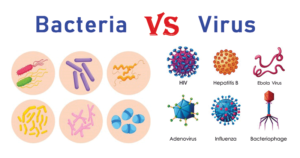
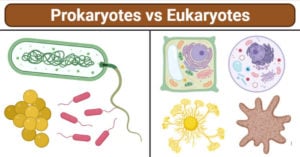
Microbiology History and Scientists with their Discoveries
Zacharias Janssen (1570-1638) Robert Hooke (1635-1703) Antony van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723) Van Helmont (1580-1644) Francesco Redi (1626-1697) Louis Joblot (1645-1723) John Needham (1713-1781) Lazzaro Spallanzani (1729-1799) F. Schulze T. Schwann H. … Read more