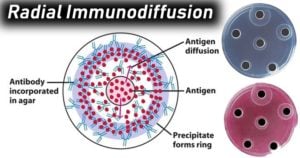
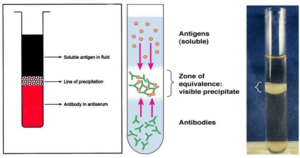
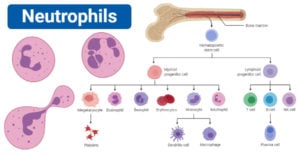
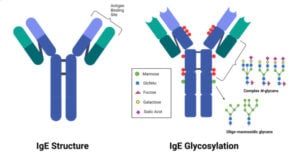
Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) Test
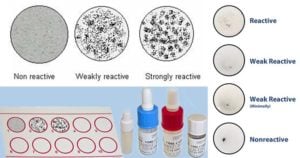
Principle of VDRL Test The Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) tests are slide microflocculation test that detect antibodies produced against antigens released by damaged host cells in patients suffering from … Read more