The health disorder caused by a successful invasion, multiplication, and establishment of pathogenic microorganisms and/or harmful microbial products on or within the host’s body cells or system is called infection. Simply, it can be defined as a disease caused by microorganisms. Infection is also called an infectious disease or communicable disease or transmissible disease.
Infections account for more than 13 million deaths each year; 13.7 million death in 2019 (G. Authia, S. Fablina, 2022). Among these 13.7 million deaths, 7.7 million are associated with bacterial infections. Due to the rapid emergence and spread of antimicrobial resistance, the case severity and mortality associated with infectious diseases are also increasing.
Infections can be classified on several bases; like microorganisms involved, presence of symptoms, anatomic location, etc. In this article, we will look over some common infections based on anatomic location i.e. organ/system involved along with their causative agents.
Interesting Science Videos
Infections of the Blood Circulatory System
These are the infections associated with the cardiovascular system including blood i.e. infection of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. It is also called bloodstream infections or infections of the blood circulatory system. Some of the common infections associated with cardiovascular systems are:
| Name of Disease | Microorganisms Involved | Description |
| Infective Endocarditis/Bacterial Endocarditis | Staphylococcus aureus Viridans Streptococci Enterococcus faecalis Enterococcus faecium Streptococcus bovis Staphylococcus epidermidis HACEK group (Haemophilus spp., Aggregatibacter spp., Cardiobacterium hominis, Eikenella corrodens, and Kingella spp.) Some minor bacterial pathogens involved are: Pseudomonas spp.Clostridium septicumBartonella spp., Chlamydia psittaci, Coxiella spp., Cutibacterium spp., Citrobacter koseri, Tropheryma whippei, etc. | Infection of endothelium i.e. inner lining of heart chambers and valves. It most commonly includes infection in the lining of heart valves. |
| Fungal Endocarditis | Candida albicans Histoplasma capsulatum Aspergillus spp. | Fungal infection of endothelium; most commonly heart valves |
| Rheumatic Heart Disease | Streptococcus spp. mainly Group A Streptococcus spp. | Infection of heart valves associated with rheumatic fever |
| Bacteremia and Septicemia – Primary bacteremia – Secondary bacteremia | Staphylococcus spp. (mainly S. aureus),Streptococcus spp. (S. pneumoniae, Viridans Streptococci,),Enterococcus spp. (mainly E. faecalis),E. coli, Pseudomonas spp., Haemophilus spp., Neisseria spp., Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella spp., Enterobacter spp., Proteus mirabilis, Listeria monocytogenes, etc. | Bacteremia simply means the presence of viable bacteria in the bloodstream Septicemia means the entering of viable bacteria into the blood and establishing infection i.e. bacteremia leading to sepsis |
| Viremia | Hepadnaviruses, flaviviruses, enteroviruses, and togaviruses are commonly found circulating in the human bloodstream. Common viruses include: HIV, Influenza viruses, Dengue virus (DENV), Zika virus, Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Hepatitis B and C viruses, Ebola virus, West Nile Virus, Varicella-Zoster virus (VZV) | Presence of viruses in the bloodstream. Most viruses are introduced in the bloodstream from other localized viral infection sites or infected organs. Viremia leads to the dissemination of viruses in the body resulting in a systemic viral infection. |
| Fungemia | Candida spp. (mainly C. albicans) Saccharomyces spp. (mainly S. boulardii), Cryptococcus spp., Aspergillus spp., Rhodotorula spp. | Presence of viable fungi (yeasts and molds) in the bloodstream. Candidemia is the most common type of Fungemia. Candidemia is the presence of Candida spp. in the bloodstream |
| Parasitic Infections of BloodStream (Some common infections associated with parasites infecting blood cells are: Babesiosis, Malaria, Leishmaniasis, Toxoplasmosis, Trypanosomiasis, Schistosomiasis) In infections like Filariasis, Onchocercasiasis, etc. parasites are present in the bloodstream) | Babesia microti Plasmodium spp. Leishmania spp. (mainly L. donovani) Toxoplasma spp. (mainly T. gondii) Trypanosoma spp. (mainly T. brucei, T. cruzi) Brugia malayi, B. timori Onchocerca volvulus Schistosoma haematobium Wuchereria bancrofti | It is the infection of blood cells by parasites like protozoans (hemoprotozoans), nematodes, Platyhelminthes, etc.). The infections may be limited to blood cells or may infect other organs along with blood cells. |
Infection of the Digestive System
The digestive system is the body system involved in food digestion. It includes the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) and associated digestive organs. The GI tract is open at both ends and is the docking place for foreign, possibly contaminated materials including foods and drinks. This makes the digestive system highly vulnerable to infection.
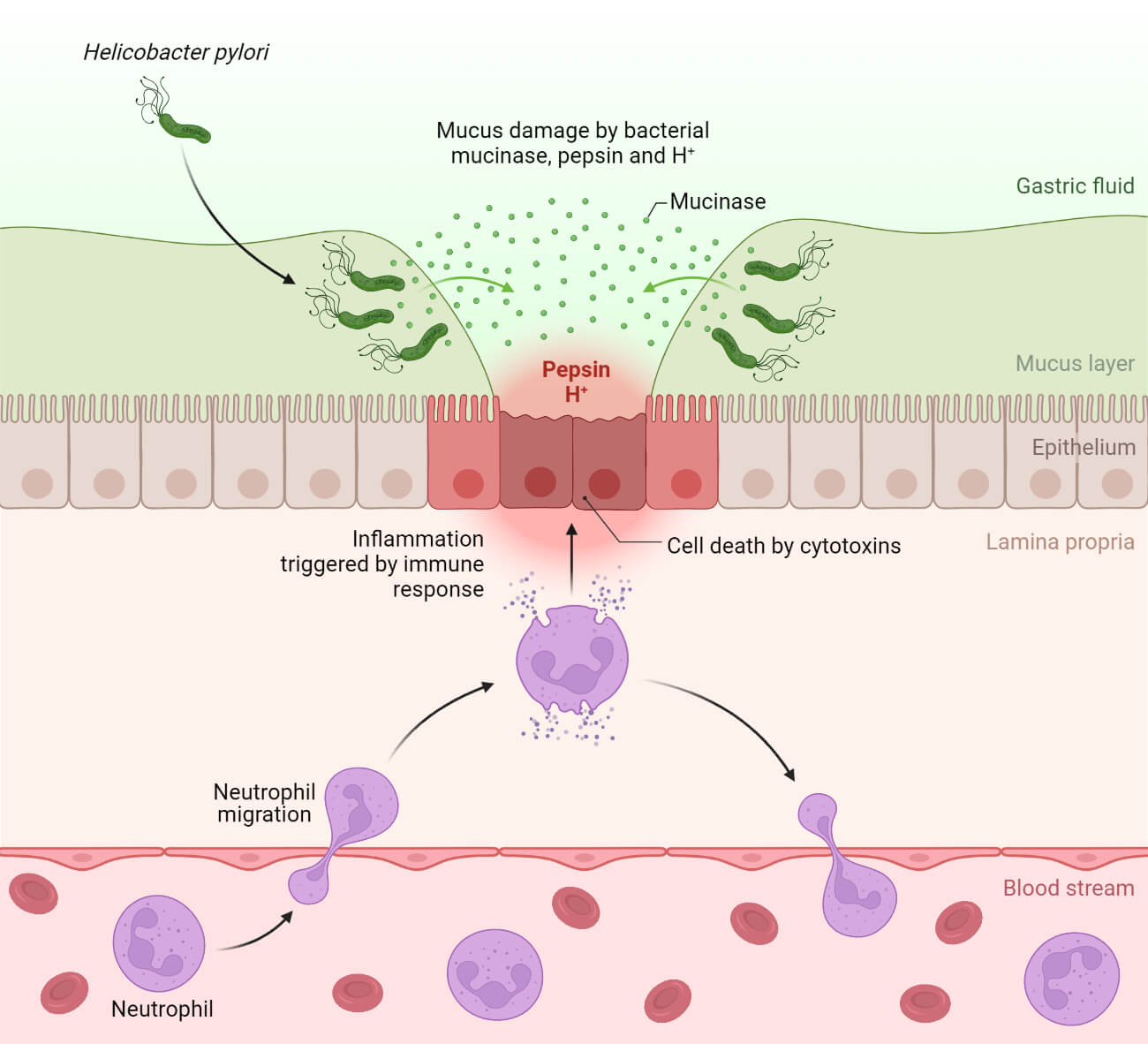
Infection of the digestive system includes infection in any section of the GI tract (from mouth to anal opening) and any digestive organs like the liver, pancreas, and gall bladder. The digestive system is infected by bacteria, viruses, protozoans, and parasites, and less frequently by fungal pathogens.
| Name of Disease | Microorganisms Involved | Description |
| Gastroenteritis – Bacterial gastroenteritis (Salmonellosis, Shigellosis, Yersinia enteritis, Campylobacteriosis, etc.) – Viral gastroenteritis – Parasitic gastroenteritis – Fungal gastroenteritis | Bacteria: E. coli, Campylobacter spp., Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Clostridium difficile, Yersinia enterocolitica, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Aeromonas spp., etc. Viruses: Rotaviruses, Noroviruses, Adenoviruses, and Astroviruses Parasites: Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica, Cryptosporidium spp., etc. Fungi: Candida spp. | Gastroenteritis is an infection of the intestine and stomach. It is commonly called the “stomach flu”. Viral gastroenteritis is the most common form of gastroenteritis. |
| Diarrhea – Bacterial Diarrhea – Viral Diarrhea | Bacteria: E. coli, Salmonella spp., Shigella flexneri, Campylobacter spp., etc. Virus: Rotaviruses, Noroviruses, Adenoviruses | It is the condition of passing loose, watery stool frequently (often more than 3 times a day). It is the most common manifestation of gastrointestinal infection. |
| Dysentery – Amoebic dysentery – Bacillary dysentery | Shigella spp. (S. dysenteriae) Entamoeba histolytica E. coli O157:H7 (EHEC) | It is the condition of severe diarrhea along with blood sometimes along with the mucus. Dysentery associated with Entamoeba is called amoebic dysentery, while dysentery caused by Shigella is termed bacillary dysentery. |
| Cholera | Vibrio cholerae | Cholera is the acute infection of the small intestine by strains of Vibrio cholerae resulting in severe acute diarrhea. |
| Typhoid and Paratyphoid | Salmonella enterica subspp. enterica serovar Typhi Salmonella enterica subspp. enterica serovar Paratyphi | It is the infection of the small intestine, liver, spleen, and gall bladder by Salmonella Typhi and Salmonella Paratyphi strains. |
| Food Poisoning Clostridial Food Poisoning Staphylococcal Food Poisoning Bacillus Food Poisoning Campylobacter Food Poisoning Fungal Food Poisoning (Aflatoxicosis) | Bacteria: Campylobacter jejuni, Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium botulinum, Bacillus cereus, Salmonella enteritis, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, Shigella flexneri, Brucella spp., etc. Fungi: Aspergillus parasiticus, Aspergillus flavus, Alternaria spp., Fusarium spp., etc. | It is a gastrointestinal disease caused by the ingestion of toxins produced by microorganisms or toxins synthesized by ingested microorganisms in the GI tract. It results in vomiting, diarrhea, dysentery, abdominal pain, fever, paralysis, and even death. |
| Infectious Colitis | Bacteria: Campylobacter spp., E. coli, Clostridium difficile, Yersinia spp., Non-typhoidal Salmonella spp., etc. Viruses: Rotaviruses, Noroviruses, Adenoviruses | It is the inflammation of the large intestine (colon) due to infection at its inner lining. |
| Helicobacter pylori infection (H. pylori Peptic Ulcer) | Helicobacter pylori | It is the formation of open sores (damage in the outer lining) in the lining of the stomach and upper part of the small intestine. |
| Infectious Hepatitis – Viral Hepatitis – Bacterial Hepatitis – Parasitic Hepatitis | Viruses: Hepatovirus (Hepatitis virus) A, B, C, D, and E Epstein-Barr virus Bacteria: Neisseria spp., Bartonella spp., Borellia spp., E.coli, Brucella spp., Campylobacter spp., Rickettsia spp., etc. Parasites: Plasmodium spp., Leishmania spp., Trypanosoma cruzi, E. histolytica, Fasciola hepatica, etc. | Hepatitis is the inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis due to any infectious agent is termed infectious hepatitis. Viral hepatitis is the most common form of infectious hepatitis. |
| Pancreatitis (Infectious Pancreatitis) | Viruses: Cytomegalovirus, Hepatitis B virus, Coxsackie virus, Varicella-zoster virus, etc. Bacteria: Salmonella spp., Legionella spp., Mycoplasma spp., etc. Parasites: Toxoplasma spp., Cryptosporidium spp., etc. | Pancreatitis is the inflammation of the liver. Pancreatitis due to any infectious agent is termed infectious hepatitis. |
| Infectious Proctitis | Viruses: Herpes Simplex virus 1 and 2, Bacteria: Treponema pallidum, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia spp., | It is the infection of the lining of the rectum and the anus leading to inflammation. |
| Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) | Enteric bacteria | SIBO means the excessive growth of bacteria in the small intestine disturbing digestion or even causing conditions like diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, indigestion, etc. |
| Protozoan Infection of the Digestive System – Giardiasis – Amoebiasis – Cryptosporidiosis – Cyclosporiasis | Giardia spp. (mainly G. lamblia) Entamoeba histolytica, Cryptosporidium parvum, C. hominis, Cyclospora cayetanensis | It includes infection of the digestive system by protozoa. |
| Helminthic Infection of the Digestive System (Helminthiasis/Worm infection) – Nematodiasis – Cestodiasis – Trematodiasis | Nematodes (Roundworms): Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris spp., Ancylostoma duodenale, Necator americanus, Trichostrongylus spp. Cestodes (Tapeworms): Taenia spp., Echinococcus spp., Hymenolepis spp. Trematodes (Flatworms): Fasciola hepatica, Clonorchis sinensis | It includes infection of the digestive system by worms (helminths). Nematodiasis is an infection by roundworms. Similarly, infections by tapeworms and flatworms are called cestodiasis and trematodiasis respectively. |
Infection of the Respiratory System
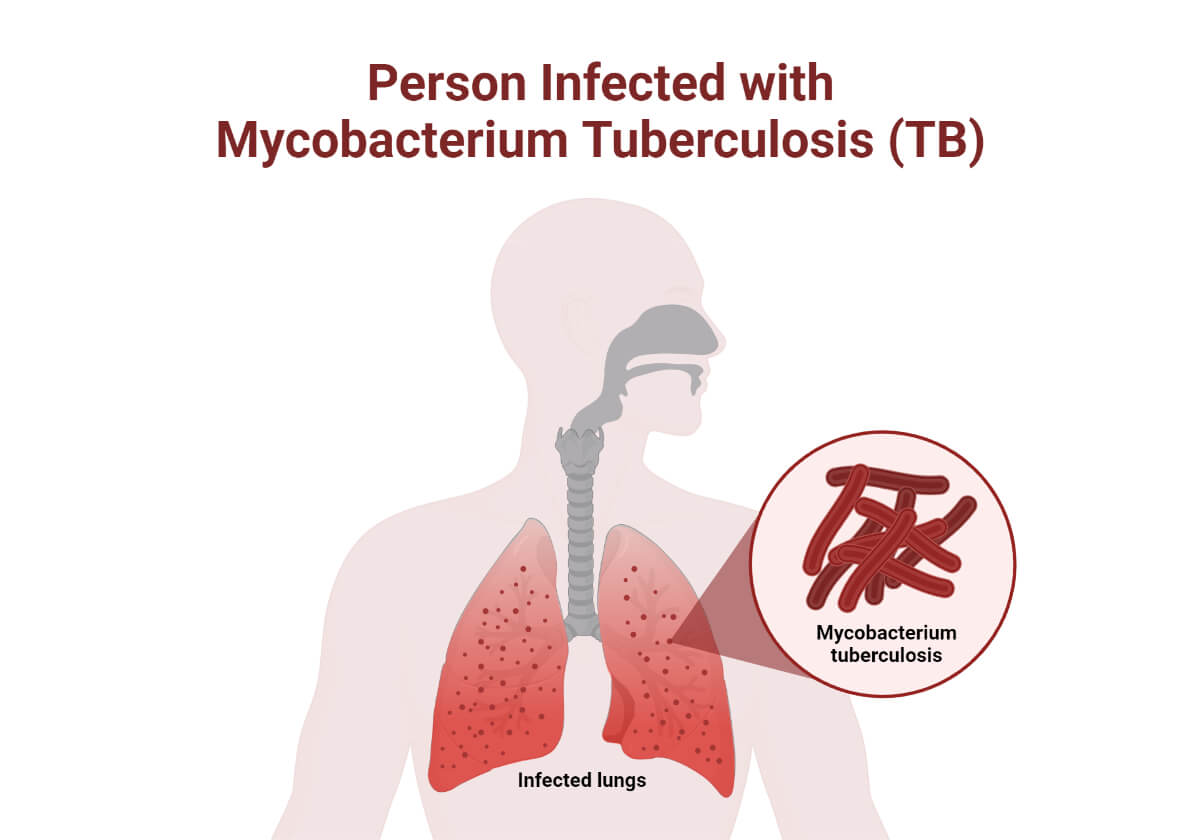
Respiratory tract infections (RTIs) are infections of any organs of the respiratory system. It is the most common type of infection in humans. Based on the parts of the respiratory tract infected, RTIs are classified as either upper RTIs (URTIs)( i.e. infection of nose, sinus, pharynx, and larynx) and lower RTIs (LRTIs) (i.e. infection of the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and lungs).
| Name of Disease | Microorganisms Involved | Description |
| Common cold | Viruses are responsible for the common cold. The most common virus involved (up to about 80% cases) is strains of Rhinovirus. Others include; coronaviruses, adenoviruses, influenza viruses, and enteroviruses. | The most common but trivial infection of the mucosal membrane of the upper respiratory tract. |
| Pneumonia | Bacteria: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, Moraxella catarrhalis, S. aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virus: Coronaviruses, Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza virus, parainfluenza virus, adenovirus Fungi: Histoplasma capsulatum, Blastomyces spp., Pneumocystis jiroveci, Coccidioides immitis, Cryptococcus neoformans | It is the acute respiratory infection of the lungs leading to the inflammation of the lungs and filling of alveoli with pus, mucus, or any fluid. |
| Pulmonary Tuberculosis | Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex | Infection of lung tissues by Mycobacterium spp. |
| Flu (Influenza) | Influenza viruses | Infection of respiratory systems by the influenza virus. |
| Diphtheria | Corynebacterium diphtheriae | Infection of nose and throat region by Corynebacterium diphtheriae |
| Infective Sinusitis | Viruses: Rhinoviruses, Coronavirus, Influenza virus, RSV, Parainfluenza virus Bacteria: Streptococcus pneumoniae, H. influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, S. aureus | Inflammation of mucous membrane lining the sinuses (air-filled chamber of nasal cavity) |
| Infective Tonsillitis, Pharyngitis, Laryngitis | Bacteria: Group A Streptococci, Neisseria spp., Corynebacterium diphtheriae, H. influenzae, Mycoplasma spp., Fusobacetrium spp., Bacillus spp., Bordetella spp. Viruses: Rhinoviruses, Adenoviruses, Measles virus, Influenza virus, Parainfluenza virus, Epstein-Barr virus, RSV, HSV, Coxsackievirus, Coronaviruses | Tonsillitis – Inflammation of tonsils. Pharyngitis – Inflammation of the pharynx.Laryngitis – Inflammation of the larynx. |
| Bronchitis | Viruses: RSV, Rhinoviruses, Adenoviruses, Influenza viruses, Coronaviruses, Metapneumoviruses, Parainfluenza viruses Bacteria: Moraxella catarrhalis, Bordetella pertussis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Viridans Streptococci, etc. | Inflammation of bronchi and bronchioles |
| Pulmonary Cryptococcosis | Cryptococcus neoformans, Cryptococcus gattii | Infection of the lungs by the fungi Cryptococcus leads to severe pneumonia. |
| Histoplasmosis | Histoplasma capsulatum Histoplasma duboisii | Infection of the lungs by the fungi Histoplasma |
| Pulmonary Coccidioidomycosis | Coccidioides immitis, Coccidioides posadasii | Infection of the lungs by the fungi Coccidioides leads to pneumonia. |
| Pulmonary Candidiasis | Candida spp. (mainly Candida albicans) | Formation of invasive lesions and foci in lungs and respiratory tract by Candida spp. |
| Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) COVID- 19 | Coronaviruses (SARS-coronaviruses, MERS-coronaviruses, SARS-CoV2) | Infection of lungs and respiratory tract by coronaviruses |
Infection of the Nervous System
Nervous system infection is any form of infection in the brain, spinal cord, and/or nerves of our body. Such neurological infections are potentially life-threatening. They are caused by different microorganisms, mostly viruses, and bacteria.
| Name of Disease | Microorganisms Involved | Description |
| Encephalitis – Bacterial encephalitis – Viral encephalitis – Parasitic encephalitis | Bacteria: Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus spp., Bartonella henselae, Mycoplasma spp., Rickettsia, etc. Viruses: Japanese encephalitis (JE) virus, Dengue viruses, Chikungunya virus, Enteroviruses, HSV, Tick-borne encephalitis virus, West Nile virus, Zika virus, Murray valley encephalitis virus, Epstein-Barr virus, Cytomegaloviruses, VZV, East equine encephalitis virus, HIV, etc. Parasites: Plasmodium spp., Toxoplasma spp., etc. | Inflammation of encephalon (brain) i.e. part of CNS inside the cranium. |
| Meningitis – Bacterial meningitis – Viral meningitis | Bacteria: Group B Streptococci (Streptococcus agalactiae), E. coli, Listeria monocytogenes, Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, etc. Viruses: Enteroviruses, West Nile virus, HSV I and II, VZV, Mumps virus, Measles virus, Lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) virus, HIV, etc. | Inflammation of meninges (the protective covering of brain and spinal cord). |
| CNS Toxoplasmosis/Cerebral Toxoplasmosis | Toxoplasma gondii Toxoplasma encephalitis | Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord by Toxoplasma. |
| Central nervous system (CNS) tuberculosis (Tuberculous meningitis) | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Infection of CNS by Mycobacterium spp. It demonstrates meningitis, tuberculoma, and spinal arachnoiditis. |
| Naegleriasis (Amoebic meningoencephalitis) | Naegleria fowleri | Inflammation of meninges and encephalon by Naegleria fowleri. |
| Cryptococcal meningitis | Cryptococcus neoformans Cryptococcus gattii | Meningitis due to the fungi Cryptococcus spp. |
| Neuroborreliosis | Borrelia spp. | Neurological manifestation of Lyme disease. |
| Rabies | Rabies lyssavirus | Infection of meninges, brain, spinal cord, and nerves by the rabies virus. |
| Poliomyelitis | Poliovirus (Enterovirus C) | Infection of nerves by Poliovirus |
| Brain abscess | Bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus spp., Pseudomonas spp., Bacteroides spp., Fusobacterium spp., Nocardia spp., Mycobacterium spp. Fungi: Cryptococcus spp., Candida spp., Blastomyces spp., Aspergillus spp., Mucorales spp., etc. Parasites:Toxoplasma spp., Trypanosoma spp. | It is the collection of pus within brain tissues. They are commonly caused by bacteria. |
Infection of the Urinary System
The urinary system includes the urethra, urinary bladder, ureters, and kidneys. Infection of any of these organs is called urinary tract infection (UTI). UTIs are mainly caused by bacteria, but rarely fungal and viral UTIs are also reported. UTIs are more provident in females than in males due to their shorter urethra.
| Name of Disease | Microorganisms Involved | Description |
| Cystitis | Uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC), S. aureus, Klebsiella spp., Proteus spp., Salmonella spp., Ureaplasma spp., Mycoplasma spp., Streptococcus spp., Serratia spp., Citrobacter spp., Candida spp., etc. | It is the infection and inflammation of the urinary bladder. |
| Pyelonephritis | UPEC, S. aureus, Neisseria spp., Streptococcus spp., Enterococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Providencia spp., Bacteroides spp., etc. | It is the infection and inflammation of the kidneys and ureters. |
| Urethritis | UPEC, S. aureus, Klebsiella spp., Proteus spp., Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Neisseria spp., Serratia spp., Candida spp., Lactococcus spp., etc. | It is the infection and inflammation of the urethra. |
Infection of the Reproductive System
The reproductive system includes all the organs involved in the reproduction process. It is in close proximity to the urinary system in humans. Many microorganisms causing UTIs are responsible for the infection of the reproductive system. The infection of the reproductive system is classified into three types: sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), endogenous infection (infection by overgrowth of microbes in the urogenital tract), and iatrogenic infections (infections by improper medical care and invasion of foreign microorganisms).
| Name of Disease | Microorganisms Involved | Description |
| Gonorrhea | Neisseria gonorrhoeae | Sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
| Syphilis | Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum | STD caused by Treponema pallidum marked by the development of painless sores in genitals and/or mouth. |
| Chlamydia (Chlamydia infection) | Chlamydia trachomatis | STD caused by Chlamydia trachomatis |
| Chancroid | Haemophilus ducreyi | STD is marked by the development of painful sores in the genitals. |
| Genital ulcer | Haemophilus ducreyi, Herpes simplex virus | Formation of open sores/ulcers in genitals. |
| Trichomoniasis | Trichomonas vaginalis | An STD parasitic infection caused by Trichomonas vaginalis characterized by foul vaginal discharge in women and mostly asymptomatic cases in males. |
| Vaginosis and vaginitis – Vaginal Candidiasis – Bacterial Vaginosis/Vaginitis | Fungi: Candida albicans, C. krusei, C. tropicalis Bacteria: Gardnerella spp., Neisseria spp., Chlamydia spp., Campylobacter spp., Mycoplasma spp. Viruses: Herpes simplex virus | Vaginosis is the excessive growth of bacteria in the vagina. Vaginitis is the infection of the vagina and vulva leading to inflammation and irritation in those areas. |
| Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) | Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Bacteroides spp., Streptococcus spp., Prevotella spp., Gardnerella vaginalis, Acinetobacter spp. | It is the infection of the upper reproductive organs of the female reproductive system. The organs infected are the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. |
| Genital Herpes | Herpes simplex virus 2 (HSV 2) | Formation of blisters progressing into ulcers around genitalia by HSV. |
| Genital Warts | Human papillomavirus (HPV) | Development of warts (keratinized or soft warts) around genitals and anal regions. |
Infection of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and lymph organs inside which lymph flows. It is a part of the immune system as well as part of the circulatory system. Lymphatic infections are not common, but several bacterial and parasitic infections are reported.
| Name of Disease | Microorganisms Involved | Description |
| Infective Lymphangitis – Infective Lymphadenopathy – Infective Lymphadenitis | Bacteria: Group A Streptococci (Streptococcus pyogenes) and other Streptococci, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Treponema pallidum, Staphylococcus spp., Rickettsia spp., Nocardia spp., etc. Fungi: Sporothrix schenckii, Scedosporium spp., etc. | Infective lymphangitis is the infection of lymphatic vessels. Inflammation of lymph nodes is called lymphadenopathy. Infection on multiple lymph nodes is called lymphadenitis. |
| Lymphatic filariasis (Elephantiasis) | Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, Brugia timori | Infestation of filarial worms in lymphatic vessels obstructing the normal lymph flow. |
Infection of Integumentary System
The integumentary system includes all the external covering of a body. It includes skin, hair, and nails. The integumentary system is the first layer of defense for our body. It is the house of millions of microorganisms as normal flora. Pathogens first come in contact with integuments before invading the body. Hence, the integumentary system gets infected time and again.
| Name of Disease | Microorganisms Involved | Description |
| Herpes Infection – Herpes labialis (Cold sores) | Herpes simplex virus | Development of fluid-filled blisters around the mouth or in lips. |
| Acne (Infectious acne) – Bacterial acne – Fungal acne | Bacteria: Cutibacterium acnes, Staphylococcus spp. Fungi: Malassezia spp. | Formation of nodules, pustules, or papules due to clogging of hair follicles. |
| Impetigo | Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes | Bacterial infection of the epidermis forms pyogenic sores or crusts in the skin. |
| Cellulitis and Folliculitis | Bacteria: Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Bacteroides spp., Haemophilus spp., Aeromonas spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pasteurella spp., Eikenella spp., etc. Fungi: Malassezia spp., Trichophyton rubrum, Candida spp., etc. | Cellulitis is the bacterial infection of dermal and/or subcutaneous layers of skin. Folliculitis is the infection of hair follicles. It is mostly by bacteria but fungi are also involved. |
| Erysipelas | Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus aureus | Infection of the upper layer of the dermis and lymphatic vessels forming a raised red rash. |
| Necrotizing fasciitis | Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus spp., Bacteroides fragilis, anaerobic E. coli, Clostridium spp., Aeromonas hydrophila, etc. | Destruction of soft tissues. |
| Rubella | Rubella virus | Skin infection by the Rubella virus leads to the formation of red rashes. |
| Skin ulcers and wounds | Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Actinomyces spp., Pseudomonas spp., Haemophilus spp., etc. | Formation of sores in the skin and destruction of the skin of that area. |
| Tinea versicolor | Malassezia furfur, Malassezia globosa | Formation of white colored patches on skin by fungi Malassezia. |
| Dandruff | Malassezia furfur | Flaking of skin; mostly of the scalp. |
| Tinea (Ringworm infection) | Trichophyton spp., Microsporum spp., Epidermophyton spp. | Formation of red, itchy, and mostly circular rash. |
| Cutaneous candidiasis | Candida albicans, C. glabrata, C. rugose, C. auris, C. tropicalis, etc. | Skin infection caused by Candida spp. |
| Warts | Human papilloma virus (HPV) | Skin bumps or lesions caused by Human papillomavirus (HPV) |
| Chickenpox | Varicella zoster virus (VZV) | Itchy red rashes by VZV. |
| Hand, foot, and mouth (HFM) disease | Enteroviruses, Coxsackieviruses | Formation of flat, discolored rashes or spots on the skin of hands, feet, and mouth area. |
Infection of the Muscular System
The muscular system includes all the muscles of our body. Infections of muscles are generally hematogenous or contagious spread, but they are usually serious and need immediate treatment.
| Name of Disease | Microorganisms Involved | Description |
| Myonecrosis (Gas gangrene) | Clostridium spp., Streptococcus spp., Bacteroides spp., Klebsiella pneumoniae, Aeromonas hydrophila, etc. | Necrotic damage of muscle tissues with the formation of tissue gas. |
| Infectious myositis and pyomyositis | Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Neisseria spp. | Myositis is the inflammation of muscles. Pyomyositis is the inflammation of muscle along with the production of pus. |
Infection of the Skeletal System
Infection of the skeletal system includes bone infection. Bone infection is not common, but it is very serious, even fatal if left untreated.
| Name of Disease | Microorganisms Involved | Description |
| Infectious osteomyelitis | Staphylococcus spp. (mainly Staphylococcus intermedius), Bacteroides spp., Actinomyces spp., Clostridium spp., Fusobacterium spp., Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp. | Infection of bone leads to its swelling. |
| Septic arthritis | Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Pasteurella spp., Mycoplasma spumans, Borrelia spp., Mycobacterium tuberculosis, etc. | Infection of bones in joints. |
| Skeletal Tuberculosis (Bone Tuberculosis) | Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex | Extrapulmonary tuberculosis of bones. |
| Mycotic bone infections (Mycotic osteomyelitis and Mycotic arthritis) | Cryptococcus neoformans, Aspergillus spp., Fusobacterium spp., Histoplasma capsulatum, Coccidioides immitis, etc. | Infection of bones and joints by fungal pathogens. |
Infection of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system is composed of endocrine glands. Infections of endocrine glands are mainly due to the hematogenous spreading of infection or progressive systemic infection.
| Name of Disease | Microorganisms Involved | Description |
| Pituitary abscess | Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., E. coli, Neisseria spp. | It is a rare infection of the pituitary gland leading to its swelling and pus formation. |
| Thyroiditis – Acute suppurative thyroiditis – Subacute thyroiditis | Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus spp., Haemophilus spp., Moraxella spp., Nocardia spp., Klebsiella spp. | It is the inflammation of thyroid glands due to infection. |
| Infectious epididymitis | N. gonorrhoeae, C. trachomatis | Inflammation of epididymis |
| Tubo-ovarian abscess | Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Bacteroides spp., Streptococcus spp., Prevotella spp., Gardnerella vaginalis, Acinetobacter spp. | Infection of fallopian tubes and ovaries leads to inflammation and pus formation. |
| Tuberculosis of the adrenal | Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium avium intracellular | Tuberculosis of the adrenal gland. |
References
- Murray, P.R., Rosenthal, K.S., & Pfaller, M.A. (2015). Medical microbiology (8th ed.). Elsevier.
- Fauci, A.S., Braunwald, E., Kasper, D. L., Hauser, S. L., Longo, D. L., & Jameson, J. L. (Eds.). (2008). Harrison’s principles of internal medicine (17th ed.). McGraw-Hill Medical
- Mandell, G. L., Bennett, J. E., & Dolin, R. (2010). Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s principles and practice of infectious diseases (7th ed.). Churchill Livingstone.
- Brook, I. (2013). Microbiology and management of respiratory tract infections. CRC Press.
- Control of Communicable Diseases Manual by David Heymann.
- G. Authia, S. Fablina, 2022. Global and regional sepsis and infectious syndrome mortality in 2019: a systematic analysis. Published by Elsevier Ltd. Published:March, 2022DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00131-0
- Loretta J. Bubenik (2005). Infections of the Skeletal System. , 35(5), 0–1109. doi:10.1016/j.cvsm.2005.05.001
- Morrison WB, Kransdorf MJ. Infection. 2021 Apr 13. In: Hodler J, Kubik-Huch RA, von Schulthess GK, editors. Musculoskeletal Diseases 2021-2024: Diagnostic Imaging [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2021. Chapter 15. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570145/ doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-71281-5_15
- Megran DW. Enterococcal endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;15(1):63-71. doi: 10.1093/clinids/15.1.63. PMID: 1617074.
- Roberts RB, Krieger AG, Schiller NL, Gross KC. Viridans streptococcal endocarditis: the role of various species, including pyridoxal-dependent streptococci. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Nov-Dec;1(6):955-66. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.6.955. PMID: 551516.
- Infective endocarditis: A contemporary update. Ronak Rajani, John L Klein. Clinical Medicine Jan 2020, 20 (1) 31-35; DOI: 10.7861/clinmed.cme.20.1.1
- Lamas, C. C., & Eykyn, S. J. (2003). Blood culture negative endocarditis: Analysis of 63 cases presenting over 25 years. Heart, 89(3), 258-262. https://doi.org/10.1136/heart.89.3.258
- Infective endocarditis. (2023, March 10). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infective_endocarditis
- Smith DA, Nehring SM. Bacteremia. [Updated 2022 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441979/
- Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia. “septicemia”. Encyclopedia Britannica, 23 Jun. 2022, https://www.britannica.com/science/septicemia. Accessed 23 March 2023.
- Martinez RM, Wolk DM. Bloodstream Infections. Microbiol Spectr. 2016 Aug;4(4). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.DMIH2-0031-2016. PMID: 27726765.
- Bloodstream infections. (2023, February 19). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloodstream_infections
- Akhondi H, Simonsen KA. Bacterial Diarrhea. 2022 Aug 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan–. PMID: 31869107.
- Bacterial gastroenteritis: Causes, treatment, and prevention (medicalnewstoday.com)
- Typhoid (who.int)
- Imam Z, Simons-Linares CR, Chahal P. Infectious causes of acute pancreatitis: A systematic review. Pancreatology. 2020 Oct;20(7):1312-1322. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.08.018. Epub 2020 Aug 30. PMID: 32938554.
- Giovane RA, Lavender PD. Central Nervous System Infections. Prim Care. 2018 Sep;45(3):505-518. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2018.05.007. Epub 2018 Jul 9. PMID: 30115337.
- Dian S, Ganiem AR, Ekawardhani S. Cerebral toxoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients: a review. Pathog Glob Health. 2023 Feb;117(1):14-23. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2022.2083977. Epub 2022 Jun 11. PMID: 35694771; PMCID: PMC9848325.
- Imam Z, Simons-Linares CR, Chahal P. Infectious causes of acute pancreatitis: A systematic review. Pancreatology. 2020 Oct;20(7):1312-1322. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.08.018. Epub 2020 Aug 30. PMID: 32938554.
- Santos AL, Coelho R, Silva M, Rios E, Macedo G. Infectious proctitis: a necessary differential diagnosis in ulcerative colitis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2019 Feb;34(2):359-362. doi: 10.1007/s00384-018-3185-5. Epub 2018 Nov 6. PMID: 30402768.
- Infection | definition of infection by Medical dictionary (thefreedictionary.com)
- Medical Definition of Infection (medicinenet.com)
- Infection Definition & Meaning – Merriam-Webster
- Deaths from pneumonia, by age, World, 1990 to 2019 (ourworldindata.org)
- FastStats – Infectious Disease (cdc.gov)
- Number of deaths by cause, World, 2019 (ourworldindata.org)
- Infective Endocarditis | American Heart Association
- Infective endocarditis: A contemporary update | RCP Journals
- Endocarditis – EMCrit Project
- Viremia definition, causes, signs, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment (healthjade.net)
- Viremia: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments and More (healthline.com)
- Viremia – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- Rheumatic Heart Disease: Definition, Causes, Prevention & Treatment (clevelandclinic.org)
- Rheumatic Heart Disease | Johns Hopkins Medicine
- Fungemia – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- What is Fungemia & How is it Treated? (epainassist.com)
- Fungemia. (2023, March 21). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fungemia
- 6 Parasitic Blood Infections – Warning – Scary – Parasites.org
- Parasitic Infections in Humans | NEB
- Infectious Colitis: Types and Treatments (verywellhealth.com)
- What is Viral Hepatitis? | CDC
- Hepatitis (who.int)
- Protozoan Infections of the Digestive System | Microbiology (lumenlearning.com)
- Pneumonia (who.int)
- Pulmonary Candidiasis – Causes, Symptoms and Treatment (medic-journal.com)
- Central nervous system tuberculosis: An overview – UpToDate
- Reproductive Tract Infections Reproductive Health Epidemiology Series Module 3 (cdc.gov)
