Deoxycholate Citrate Agar (DCA)- Composition, Principle, Preparation, Results, Uses
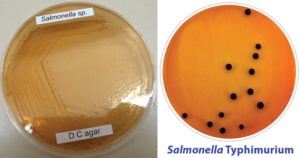
Deoxycholate Citrate Agar is a modification of Leifson formula and is recommended for the isolation of Salmonella and Shigella spp. This medium is similar to deoxycholate agar in comparison but … Read more