NYC Agar Base medium was originally developed by Fauer, Weisburd, and Wilson at the New York City Department of Health for selective isolation of pathogenic Neisseria species from clinical specimens. NYC medium, primarily designed for isolation of pathogenic Neisseria, also readily supports the growth of large-colony mycoplasmas and T-mycoplasmas (Ureaplasma). It is a transparent medium, highly selective which permits direct, microscopic observation and presumptive identification of mycoplasmas, as well as Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Interesting Science Videos
Composition of New York City Agar
| Ingredients | Gms / L |
| Proteose peptone | 15.0 |
| Corn starch | 1.0 |
| Glucose | 5.0 |
| Sodium chloride | 5.0 |
| Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate | 4.0 |
| Potassium dihydrogen phosphate | 1.0 |
| Agar | 20.0 |
Final pH ( at 25°C) 7.4±0.2
Principle of New York City Agar
NYC agar is a transparent medium, comprised of peptone, corn starch agar base buffered with phosphates and supplemented with horse plasma, horse hemoglobin, dextrose, yeast autolysate, and some antibiotics. Proteose peptone is rich in proteoses, peptones, and free amino acids which provide nutrients for the growth of the bacterium. Phosphate buffers the medium. Starch neutralizes the toxic metabolites produced by Neisseria. Sodium chloride provides essential electrolytes maintaining osmotic equilibrium thereby maintaining the integrity of cells. The selective supplement added contains the antibiotics vancomycin that inhibits gram-positive bacteria, colistin that inhibit gram-negative bacilli including Pseudomonas species, nystatin suppress yeast growth and trimethoprim lactate prevents Proteus species swarming. The combination of trimethoprim and colistin acts synergistically against gram-negative bacilli. Lysed horse blood, horse serum, yeast dialysate are the enrichments that permit a luxuriant recovery of pathogenic Neisseria species. The yeast autolysate supplement fulfills the CO2 requirements needed to enhance Neisseria growth. Yeast contains oxaloacetic acid which is metabolized by gonococci to produce sufficient CO2 for the growth of capnophilic gonococci. Also, the presence of yeast autolysate reduces the lag phase of the growth of Neisseria, thus enhancing both size and number of colonies.
Preparation of New York City Agar
- Suspend 25.50 grams in 320 ml distilled water.
- Heat to boiling to dissolve the medium completely.
- Sterilize by autoclaving at 15 lbs pressure (121°C) for 15 minutes. Avoid overheating.
- Cool to 45-50°C and add aseptically 100 ml of sedimented horse blood cells and 60 ml of citrated horse plasma along with rehydrated contents of 1 vial of NYC Supplement and 1 vial of Yeast Autolysate Supplement.
- Mix well and pour into sterile Petri plates.
Result on New York City Agar
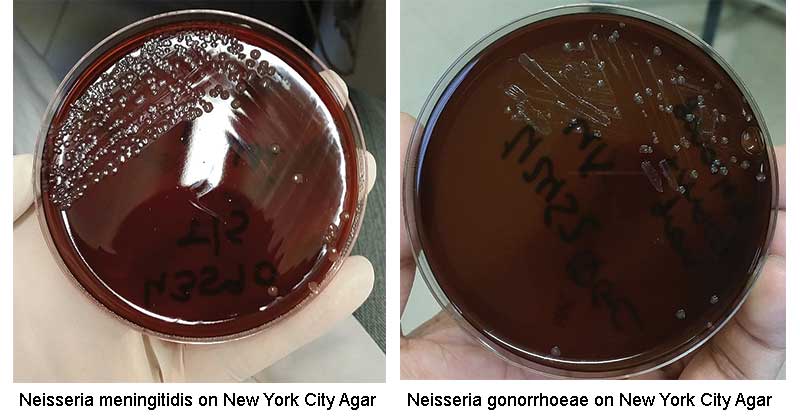
Source: Wikipedia
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae: small (0.5-1.0 mm), grayish-white to colorless, mucoid colonies.
- Neisseria meningitidis: large mucoid colonies, colorless to bluish-gray
Uses of New York City Agar
- New York City (NYC) medium is an enriched selective medium used for the isolation and cultivation of pathogenic Neisseria species.
- It is useful in gonorrhea screening programs and in the recognition of active or asymptomatic mycoplasma infections.
- The medium can be valuable in establishing the frequency of association of mycoplasmas with urogenital tract infection.
- It also supports the growth of genital mycoplasmas (Mycoplasma hominis and Ureaplasma urealyticum).
Limitations of New York City Agar
- It is recommended that biochemical, immunological, molecular and mass spectrometry testing be performed on colonies from pure culture for complete identification.
- Some strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeaeare inhibited by the concentration of vancomycin in the selective media, so the addition of nonselective chocolate agar is recommended, especially in suspect cases that are culture negative or for sterile specimens.
References
- Quelab- http://www.quelab.com/htmleng/1276a.html
- Himedia
- Granato PA, Schneible-Smith C and Weiner LB (1981). Use of New York City Medium for Improved Recovery of Neisseria gonorrhoeae from Clinical Specimens. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 13(5):963-968.
- Faur YC, Weisburd MH, Wlson ME, May PS (1974). NYC medium for simultaneous isolation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, large-colony mycoplasmas, and T-mycoplasmas. Appl Microbiol. 27(6):1041–1045.
- Anstey RJ, Gun-Munro J, Rennie RP, et al (1984). Laboratory and clinical evaluation of modified New York City medium (Henderson formulation) for the isolation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 20(5):905–908.
- Ronald M. Atlas and James W. Snyder (2014). Handbook of media for clinical and public health microbiology. CRC Press. Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
