Apoptosis- Definition, Pathways, Assay, Examples (vs Necrosis)
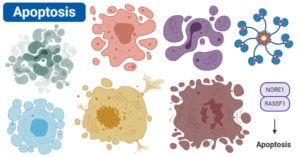
Apoptosis is a normal genetically programmed cell death where an aging cell at the end of its life cycle shrinks and its remaining fragments are phagocytosed without any inflammatory reaction. … Read more