Interesting Science Videos
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
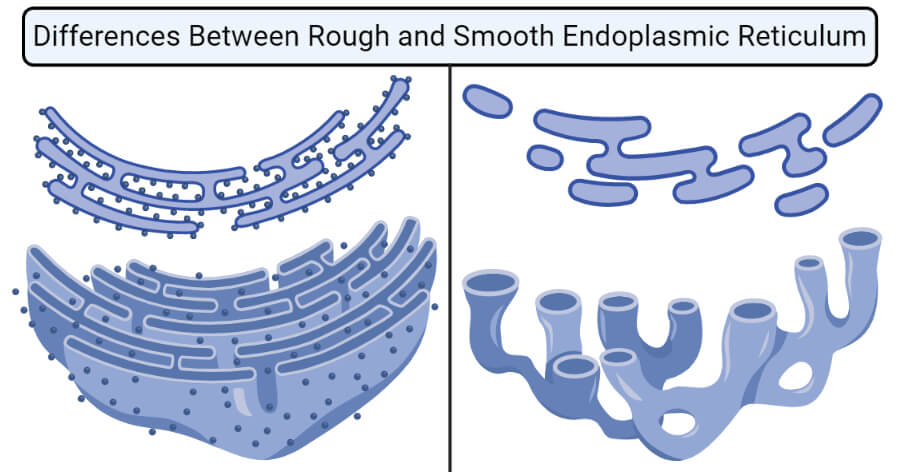
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is a type of endoplasmic reticulum consisting of flattened sacs, studded with protein-synthesizing particles termed ribosomes on the outer surface.
- The rough endoplasmic reticulum is a part of the endomembrane system that is present in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- The organelle is involved in the synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of proteins to different organelles within the cell or outside of the cell.
- The name ‘rough’ ER is given due to the appearance of ribosomes on the surface as studs under the microscope.
- Found both in plant and animal cells, the RER membrane is continuous with the nuclear membrane.
- It is usually located near the Golgi apparatus, and the protein synthesized in the ribosomes on RER are packaged into vesicles and transported to the Golgi body.
- Rough ER is primarily made up of flattened sacs called cisternae with few tubules. The membrane is also provided with an essential protein complex termed translocon, which is vital for translation within RER.
- The ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum with the help of the group of proteins, termed ribophorins.
- The structure of rough ER is based on the presence of cytoskeletal elements like microtubules, where changes in microtubules cause changes to the structure of RER.
- Besides, the ribosomes present on the rough ER often detach themselves and develop into individual cisternae.
- Within the lumen of the RER, newly formed proteins undergo slight modifications like cleavage of signal sequences and glycosylation. Some proteins might change their three-dimensional conformation within the lumen.
- Rough ER is closely associated with the formation of lysosomes.
- Also, rough ER also plays a significant role in quality control during the folding of the proteins where the ratio of sheets to tubules is changed when the quantity of unfolded proteins increases in the cell.
- Sometimes, apoptosis is initiated in the cell as a result of the increase in the content of unfolded proteins.
- Similarly, rough ER also contains multiple enzymes that are involved in RNA metabolism that function to bind and modify RNA.
- However, different diseases might result from the misfolding of proteins in RER. Disease like spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia is attributed due to the accumulation of misfolded collagen proteins in the RER.
Read Also: Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)- Definition, Structure, Functions, and Diagram
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is a type of endoplasmic reticulum consisting of tubular vesicles that lack ribosomes on the outer surface and is involved in the synthesis and storage of lipids.
- Smooth ER is a part of the endomembrane system that form important structural lipids like cholesterol and phospholipids.
- The term ‘smooth’ indicates the absence of ribosomes on the outer surface, which results in a smooth outer surface.
- Smooth ER is formed from rough ER after the shedding of the existing ribosomes of the surface.
- Smooth ER, like rough ER, is found in both animals and plants. In humans, smooth ER is prominent in the cells of the liver that produce steroid hormones.
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is mainly composed of a network of tubules. It is mostly located nearby the cell membrane.
- These structures are often associated with the formation of spherosomes or oleosomes.
- The tubular structure of smooth ER is prominent in the muscle and nerve cells in humans that form networks with other cells.
- In muscle cells, the sarcoplasmic reticulum is formed of smooth ER that are important in the accumulation of calcium ions.
- Smooth ER also has a dynamic structure that gives off new tubules from the sides. These tubules also bind with the cytoskeletal framework of the cell.
- The number of smooth ER in a cell depends on the type, location, and function of the cell. Cells of muscles and glands have a comparatively lesser number of SER.
- In the endocrine system, the smooth ER also responsible for the synthesis of steroid hormones from cholesterol.
- In the liver, it produces enzymes that catalyze reactions responsible for the removal of drugs, metabolic wastes, and harmful chemical substances. The dynamic structure of SER enables it to accumulate large quantities of harmful chemicals during detoxification.
- SER is thus essential for the detoxification of chemicals and the removal of wastes.
- Besides, the smooth ER also contains the enzyme’s glucose-6-phosphate that is important for the conversion of glycogen to glucose.
- However, prolonged SER stress might result in the development and progression of many diseases, including neurodegeneration, atherosclerosis, type 2 diabetes, liver disease, and even cancer.
Key Differences (Rough endoplasmic reticulum vs Smooth endoplasmic reticulum)
| Basis for comparison | Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) | Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) |
| Definition | The rough endoplasmic reticulum is a type of endoplasmic reticulum consisting of flattened sacs, studded with protein-synthesizing particles termed ribosomes on the outer surface. | Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is a type of endoplasmic reticulum consisting of tubular vesicles that lack ribosomes on the outer surface and is involved in the synthesis and storage of lipids. |
| Ribosomes | Rough ER has ribosomes on the outer surface. | Smooth ER doesn’ thave ribosomes on the outer surface. |
| Location | The rough endoplasmic reticulum is mostly found around the nuclear membrane. | The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is mostly found near the cell membrane. |
| Origin | Rough ER is formed from the nuclear membrane. | Smooth ER is formed after the shedding of ribosomes from rough ER. |
| Structure | Rough ER is mainly composed of cisternae with few tubules. | Smooth ER is mainly composed of a network of tubules with few cisternae. |
| Structure | Rough ER posses narrow pores below the ribosomes that allow the passage of newly synthesized polypeptides to the cytosol. | No such pores are present on the surface of the smooth ER. |
| Ribophorins | Ribophorins are present on the surface of the rough ER. | Ribophorins are absent on the surface of the smooth ER. |
| Involved in | Rough ERs are involved in the formation of lysosomes. | Smooth ERs are involved in the formation of spherosomes or oleosomes. |
| Found in | Numerous rough ER is found in lipid synthesizing cells. | Numerous smooth ER is found in protein synthesizing cells. |
| Type of cell | RER is mostly found in cells of glands and protein-producing organs. | SER is mostly found in cells like muscle cells and nerve cells. |
| Golgi apparatus | Rough ER provides proteins and lipids for the Golgi apparatus. | Smooth ER provides vesicles for the cis-face of the Golgi apparatus. |
| Function | The rough endoplasmic reticulum is mostly associated with the production, modification, and transfer of proteins. | The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is mostly associated with the production of lipids and the storage of calcium ions. |
| Diseases | Disease like spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia is attributed due to the accumulation of misfolded collagen proteins in the RER. | Prolonged SER stress might result in the development and progression of many diseases, including neurodegeneration, atherosclerosis, type 2 diabetes, liver disease, and even cancer. |
References and Sources
- Ozcan, L., & Tabas, I. (2012). Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in metabolic disease and other disorders. Annual review of medicine, 63, 317–328. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-043010-144749
- 2% – https://www.vedantu.com/biology/difference-between-smooth-endoplasmic-reticulum-and-rough-endoplasmic-reticulum
- 1% – https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/ribosome
- 1% – https://www.quora.com/How-are-the-golgi-apparatus-and-nucleus-related
- 1% – https://www.mpg.de/36350/bm10_Proteinfolding-basetext.pdf
- 1% – https://www.endocrineweb.com/endocrinology/overview-adrenal-glands
- 1% – https://vivadifferences.com/smooth-vs-rough-endoplasmic-reticulum/
- 1% – https://sciencemonk.com/endoplasmic-reticulum/
- 1% – https://quizlet.com/21343918/cell-organelles-functions-flash-cards/
- 1% – https://quizlet.com/164089069/ribosomes-flash-cards/
- 1% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rough_endoplasmic_reticulum
- 1% – https://brainly.com/question/13390727
- 1% – https://biologydictionary.net/rough-endoplasmic-reticulum/
- <1% – https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/endoplasmic-reticulum-golgi-apparatus-and-lysosomes-14053361/
- <1% – https://quizlet.com/29746816/anatomy-chapter-11-flash-cards/
