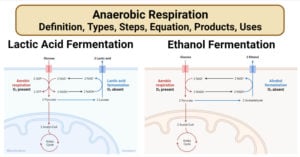
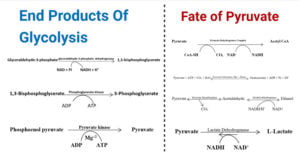
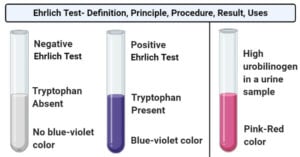
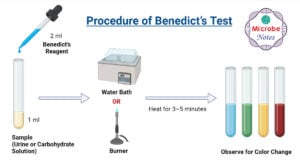
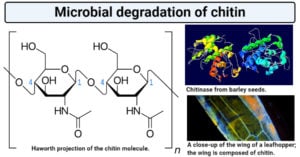
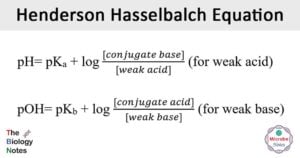
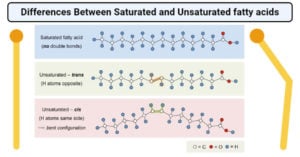
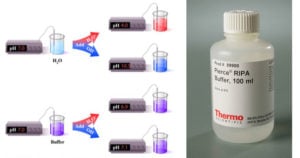
Anaerobic Respiration- Definition, Types, Steps, Equation, Products, Uses
Respiration is the metabolic process of breaking down the simple organic nutrients (food material) releasing the cellular energy in form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) inside the living cell. It is … Read more