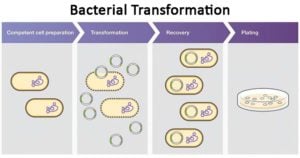
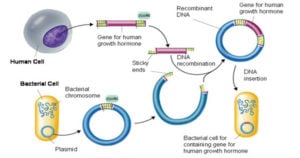
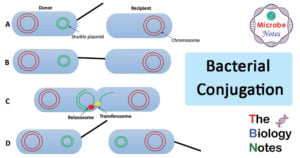
Protein Synthesis in Eukaryotes- Definition, Enzymes and Process
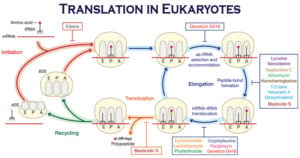
Protein Synthesis involves translating the sequence of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule to a sequence of amino acids during protein synthesis. It is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or ER synthesize proteins … Read more