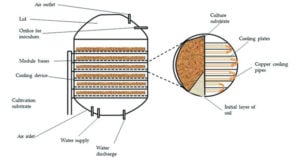
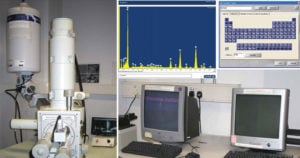
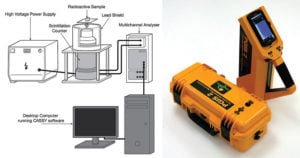
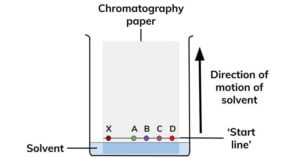
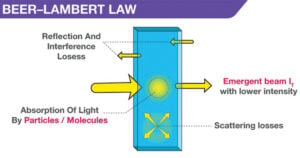
Solid State Fermentation (SSF)
Solid State Fermentation (SSF) is a fermentation method used by several industries like the pharmaceuticals, food, textile etc., to produce metabolites of microorganisms using solid support in place of the liquid … Read more