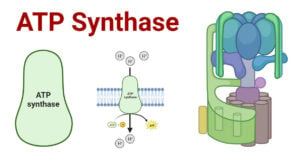
ATP Synthase: Structure, Mechanism, Significances
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) is commonly referred to as the “universal energy carrier” or “molecular currency” for energy transfer in cells. Every living thing relies on ATP generation as the main … Read more