Sarcomere: Structure, Function & Role in Muscle Contraction
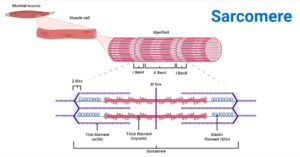
Sarcomeres are the basic contractile units of striated muscle cells. A sarcomere is a highly organized structure made up of thick and thin protein filaments; mainly of actin and myosin … Read more