Spot indole test method is a rapid indole detection method where bacteria cultivated in the tryptophan-rich medium are directly exposed to an Indole Reagent for detection of indole production.
The indole test is a biochemical test used to detect the ability of bacteria to metabolize tryptophan-producing indole. It is the first test in the IMViC test series.
Tryptophan is an amino acid that can be enzymatically degraded by some bacteria. The bacterial enzyme tryptophanase deaminates and hydrolyzes the tryptophan into three end products – indole, pyruvate, and ammonium. The produced indole can be detected easily in the lab to find out about tryptophan metabolism. The biochemical test used to find the production of indole after enzymatic hydrolysis of tryptophan is called the indole test.
An indole test is usually performed to detect and differentiate the members of the Enterobacteriaceae family.
In the lab, it can be performed following common methods; tube method and spot indole test method. In the tube method, a medium containing tryptophan is placed in a test tube and sample bacteria are inoculated on the medium. Following the incubation of about 24 hours at ambient conditions, reagents are added to check for the presence of indole in the medium.
Interesting Science Videos
Objectives of Spot Indole Test
- To differentiate bacteria based on their ability to hydrolyze tryptophan and produce indole
- To differentiate and identify members of Enterobacteriaceae
Principle of Spot Indole Test
Tryptophanase enzyme produced by some bacteria can enzymatically hydrolyze the ‘tryptophan’ amino acid present in culture medium and result in the production of indole, pyruvic acid, and ammonia.
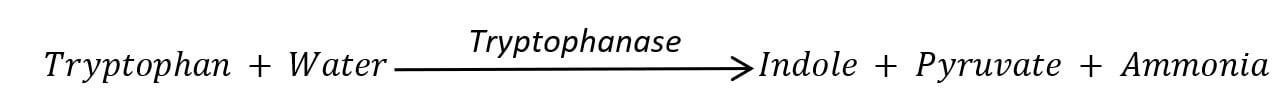
The indole thus produced will combine with the aldehyde present in the reagent to give a distinctive color (green to blue color if cinnamaldehyde reagent is used, and pink to violet-red if aldehyde reagent is used.)
Requirements for Spot Indole Test
Culture Medium
No culture medium is used for performing this rapid spot indole test.
Reagent
5% p-dimethylamino benzaldehyde or 1% p-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde in 10% (v/v) concentrated HCl for the spot indole test for testing aerobic and anaerobic organisms respectively.
5% p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde
- Add 10 mL of concentrated HCl (hydrochloric acid) in 90 mL of distilled water.
- Dissolve 5 grams of p-dimethylamino benzaldehyde in the above acid solution to form 5% p-dimethylamino benzaldehyde
1% p-Dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde
- Add 10 mL of concentrated HCl (hydrochloric acid) in 90 mL of distilled water.
- Dissolve 1 gram of p-Dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde in the above acid solution to form 1% p-Dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde.
Equipment
| Filter Paper | Dropper | Cotton Swab | Inoculating loop |
Test Organisms (Sample Bacteria)
18 to 24 hours old (Fresh) culture of bacteria grown on tryptophan-rich medium.
Control Organisms
Escherichia coli ATCC 25922
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853
Porphyromonas asaccharolytica ATCC 25260
Bacteroides fragilis ATCC 25285
Procedure of Spot Indole Test
Any of the following three procedures can be followed to perform the Spot Indole Test.
1. Filter Paper Method
- Moisten a strip of filter paper with the indole reagent.
- Using a sterile inoculating loop, pick up fresh (18 to 24 hours) colonies grown in a tryptophan-rich medium and rub the colonies over the moistened filter paper.
- Observe for color change within 20 seconds.
2. Swab Method
- Using a sterile swab, pick up some fresh (18 to 24 hours) colonies of sample bacteria grown in a tryptophan-rich medium.
- Add a drop of indole reagent directly over the colonies.
- Observe for color change within 20 seconds.
3. Direct Agar Plate Method
- Drop indole reagent directly over the fresh colonies of sample bacteria grown in tryptophan-rich medium.
- Observe the color change on the colonies and surrounding medium within 20 seconds.
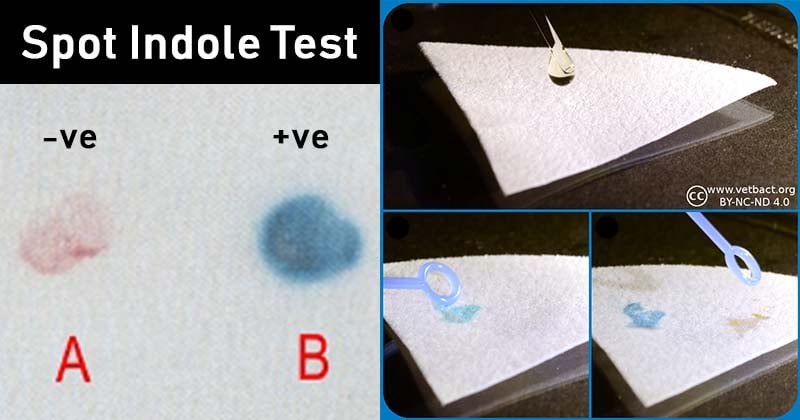
Result and Interpretation of Spot Indole Test
A positive test result is indicated by:
- Development of blue or pink to red color in the filter paper.
- Development of blue or pink to red color in the cotton swab.
- Development of blue or pink to red color over the colonies exposed with indole reagent.
(Color depends on the types of indole reagent used. If 5% p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde is used pink to violet-red color is developed. If 1% p-Dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde is used green to blue color is developed.)
A negative test result is indicated by no color change in filter paper, cotton swabs, or colonies exposed to the indole reagent.
Quality Control
- Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Porphyromonas asaccharolytica ATCC 25260 give a positive result. E. coli is used for aerobic culture control and P. asaccharolytica is used for anaerobic culture control.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 and Bacteroides fragilis ATCC 25285 gives negative result. P. aeruginosa is used for aerobic culture control and B. fragilis is used for anaerobic culture control.
Spot Indole Test Result of Some Common Bacteria
- Indole Positive Bacteria: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella oxytoca, V. cholerae, Proteus vulgaris, Porphyromonas asaccharolytica, Vibrio spp., Flavobacterium spp., Providencia spp., Enterococcus faecalis, Haemophilus influenzae, Morganella morganii, Aeromonas spp., Citrobacter koseri, etc.
- Indole Negative Bacteria: Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Citrobacter freundii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacteroides fragilis, Staphylococcus aureus, etc.
Precautions
- Always use the bacteria grown in the tryptophan-rich medium for testing.
- Read the result within 20 seconds of the addition of the indole reagent.
- Don’t use medium-containing dye/indicators like EMB, McConkey, etc.
- Use 1% p-Dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde reagent for testing anaerobic bacteria and 5% p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde reagent for testing aerobic bacteria.
Applications of Spot Indole Test
- To rapidly identify and differentiate members of Enterobacteriaceae.
- Rapid identification of bacteria.
- Rapid differentiation of K. oxytoca (indole +ve) from K. pneumoniae (indole – Ve), Citrobacter koseri (indole + ve) from C. freundii (indole – Ve), and Proteus vulgaris (Indole +ve) from P. mirabilis (indole – Ve).
Limitations of Spot Indole Test
- Spot Indole Test’s efficiency is lower than the tube indole test.
- Needs fresh culture of bacteria grown in a tryptophan-rich medium.
- Indole diffuses in nearby culture medium; hence, while performing the test directly on an agar plate the diffused indole may give a false positive result.
- Need of heavy inoculum for fastidious organisms.
- Spot Indole Test is not a confirmatory test, so requires results of other biochemical tests to completely identify the isolate.
References
- Leber, Amy L., editor in chief. (2016). Clinical microbiology procedures handbook (Fourth edition) . Washington, DC : ASM Press 1752 N St., N.W., [2016] doi:10.1128/9781555818814.ch3.17.33
- Tille, P. M., & Forbes, B. A. (2014). Bailey & Scott’s diagnostic microbiology (Thirteenth edition.) P. 185 – 187. St. Louis, Missouri: Elsevier
- Miller JM, Wright JW. Spot indole test: evaluation of four reagents. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):589-92. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.589-592.1982. PMID: 7040458; PMCID: PMC272149.
- Bale MJ, McLaws SM, Matsen JM. The spot indole test for identification of swarming Proteus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jan;83(1):87-90. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/83.1.87. PMID: 3966445.
- Darkoh, C., Chappell, C., Gonzales, C., & Okhuysen, P. (2015). A Rapid and Specific Method for the Detection of Indole in Complex Biological Samples. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 81(23), 8093-8097. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02787-15
- https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/762018/TP_19i4.pdf
- https://microbeonline.com/indole-test-principle-procedure-results/#Uses
- https://www.onlinebiologynotes.com/indole-test-objective-principle-procedure-and-result/
- https://microbiologyinfo.com/indole-test-principle-reagents-procedure-result-interpretation-and-limitations/
- https://microbiologie-clinique.com/indole-test-en.html
- https://asm.org/getattachment/200d3f34-c75e-4072-a7e6-df912c792f62/indole-test-protocol-3202.pdf
