Interesting Science Videos
Differences between antigen and antibody
Antibodies are produced by the immune system in response to antigens (material perceived as foreign). The antibody response to a particular antigen is highly specific and often involves a physical association between the two molecules. This association is governed by biochemical and molecular forces. The reaction between antigens (Ags) and antibodies (Abs) involves complementary binding sites on the Ab and on the Ag molecules. Some of the differences between antigen and antibody are as follows:
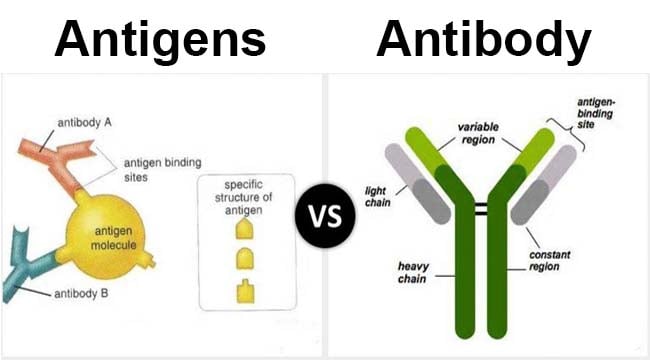
Some of the differences are:
S.N. |
Characteristics |
Antigen |
Antibody |
|
1 |
Molecule Type |
Usually, proteins may also be polysaccharides, lipids or nucleic acids. |
Proteins |
|
2 |
Definition |
These are substances that provoke an immune response. |
These are Glycoproteins that are secreted by immune cells (plasma cells) in response to a foreign substance (antigen). |
|
3 |
Effect |
Cause disease or allergic reactions. |
Protect the system by lysis of antigenic material. |
|
4 |
Origin |
Within the body or externally. |
Within the body. |
|
5 |
Parts |
Highly variable with different structural conformations and is usually composed of different epitopes. | Composed of three main parts:
-Two light chains -Two heavy chains -Four polypeptides |
|
6 |
Prevalence | Exists in all types of cells; mostly found in viruses, bacteria, and fungi. | Only present in some types of cells. |
|
7 |
Synonyms |
Immunogens |
Immunoglobulins |
|
8 |
Specific binding site |
Epitope |
Paratope |
|
9 |
Complexity |
Medium; exists due to random mutations in the cell’s gene. |
Very High; Complex chemical that bonds to a very specific Antigen. |
|
10 |
Source |
Usually from a foreign substance (viruses, and bacterial and fungal toxins). |
Naturally produced by the body (B lymphocytes or B cells). |
|
11 |
Kinds | There are three basic kinds of antigens (Exogenous, Endogenous, and Autoantigens) |
There are five basic kinds of antibodies (IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD). |
|
12 |
Examples | Exogenous antigens: bacteria, viruses, fungi, etc.
Endogenous antigens: Blood group antigens, HLA (Histocompatibility Leukocyte antigens), etc. Autoantigens: Nucleoproteins, Nucleic acids, etc. |
Breast milk, tears, saliva, sweat, and mucus. |

sir, I want you pls to expanded it more
You can find more details here https://microbenotes.com/antibody/ and https://microbenotes.com/antigen/
please sir, is it good for body have positive antigen
Sir pls note on antigens and antibodies
Sir will you please provide notes for difference between MHC class 1 and class 2 molecules