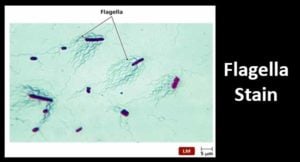
Flagella Stain- Principle, Procedure and Result Interpretation
Objective of Flagella Stain This technique is used to visualize the presence and arrangement of flagella for the presumptive identification of motile bacterial species. Principle of Flagella Stain Flagella are … Read more