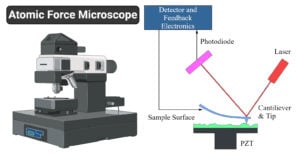
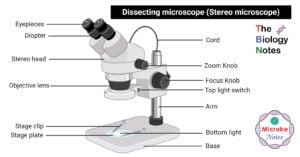
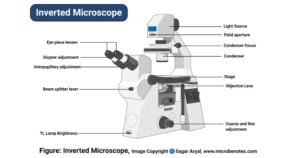
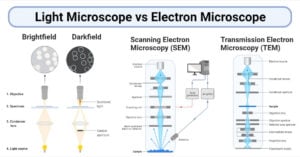
Atomic Force Microscope: Principle, Parts, Uses
The atomic force microscope (AFM) is a type of scanning probe microscope whose primary roles include measuring properties such as magnetism, height, friction. The resolution is measured in a nanometer, … Read more