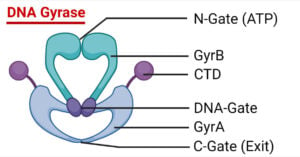
DNA Gyrase- Definition, Structure, Reactions, Mechanisms
Prokaryotic topoisomerase II, also known as DNA gyrase, is the only topoisomerase that introduces negative supercoils into DNA thus far. DNA topoisomerases are a class of enzymes that can change the … Read more