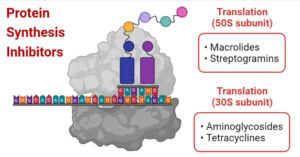
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors- Definition, Examples, Inhibition, Resistance
What are Protein synthesis inhibitors? Protein synthesis, a long process that includes different enzymes and structural change in organisms. Some antibacterial classes inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by interfering with the … Read more