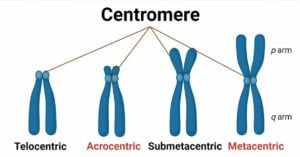
Centromere- Definition, Structure, Position, Types, Functions
The centromere is derived from the Greek words “Centro” and “mere” which mean “central” and “part” respectively. When a cell divides, the centromere, which resembles a constrictive area of a … Read more