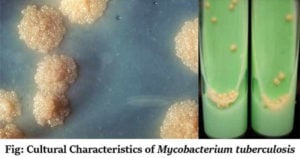
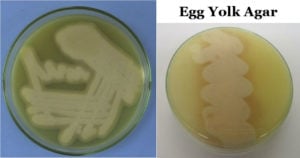
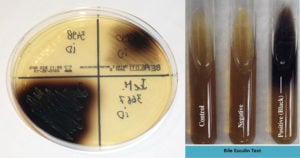
Lowenstein Jensen (LJ) Media- Composition, Principle, Preparation, Results, Uses
Lowenstein Jensen (LJ) Media is a selective medium that is commonly used for the cultivation and isolation of Mycobacterium, specifically Mycobacterium tuberculosis from clinical specimens. LJ medium was originally formulated by … Read more