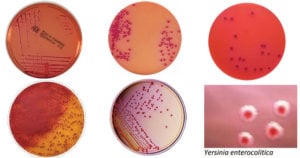
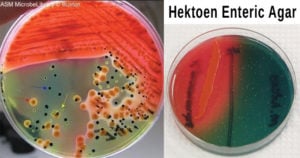
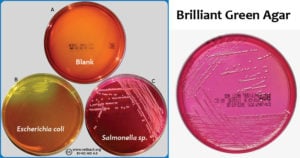
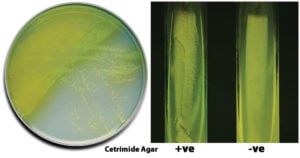
EMB Agar- Composition, Principle, Preparation, Results, Uses
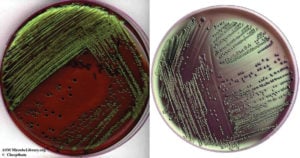
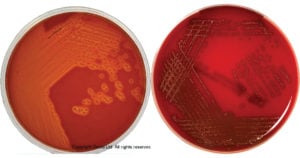
Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) agar is a differential microbiological medium, which slightly inhibits the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and provides a color indicator distinguishing between organisms that ferment lactose (e.g., E. coli) and those that … Read more