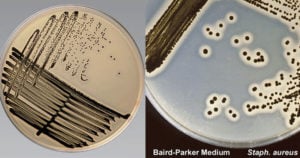
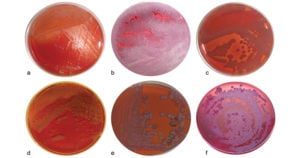
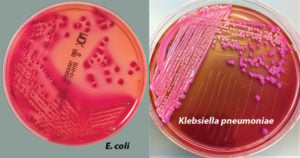
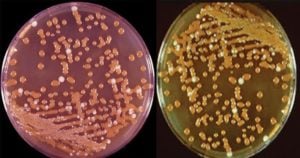
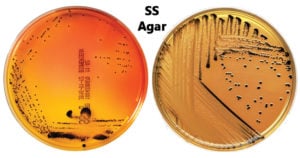
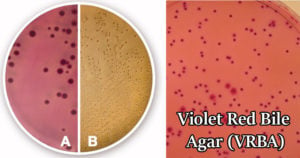
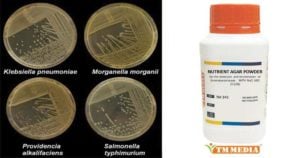
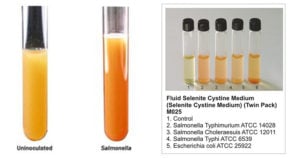
Baird Parker Agar- Composition, Principle, Preparation, Results, Uses
Baird Parker Agar was developed by Baird Parker from the Tellurite-glycine formulation of Zebovitz et al for isolation and enumeration of Staphylococci in food and other material since it allows … Read more