Brucella is an intracellular parasite that causes epizootic abortions in animals and septicemic febrile illness or localized infections of the bone, tissue, or organ systems in humans. Brucella species are highly fastidious and therefore require a nutrient-rich medium to be able to grow. Also, Brucella species are highly infective and so extreme care should be taken while handling. Brucella Agar Base with the supplement is recommended for enrichment, isolation, and cultivation of Brucella or Campylobacter species from clinical and nonclinical specimens. Brucella medium is a modified medium formulated to support a luxuriant growth of other fastidious bacteria also such as Streptococci, pneumococci, Listeria, Neisseria meningitides, and Haemophilus influenzae.
Interesting Science Videos
Composition of Brucella Agar
| Ingredients | Gms/liter |
| Enzymatic Digest of Casein | 10.00 |
| Enzymatic Digest of Animal Tissue | 10.00 |
| Yeast Extract | 2.000 |
| Sodium Chloride | 5.000 |
| Dextrose | 1.000 |
| Sodium Bisulfite | 0.100 |
| Agar | 15.00 |
Final pH: 7.0 ± 0.2 at 25°C
Principle of Brucella Agar
Brucella Agar supports the growth of fastidious microorganisms due to their content of peptones, dextrose, and yeast extract. The peptones supply organic nitrogen. The yeast extract is a potent source of the B-complex vitamins. Dextrose is utilized as an energy source. Sodium bisulfite is a reducing agent, and sodium chloride maintains the osmotic equilibrium. Agar is the solidifying agent in Brucella Agar.
Preparation and Method of Use of Brucella Agar
- Suspend 43 g of the medium in one liter of purified water.
- Heat with frequent agitation and boil for one minute to completely dissolve the medium.
- Autoclave at 121°C for 15 minutes.
- Pour into sterile Petri plates.
- Use standard procedures to obtain isolated colonies from specimens.
- Since many pathogens require carbon dioxide on primary isolation, incubate plates at 35 ± 2°C for 24-72 hours in an aerobic atmosphere supplemented with carbon dioxide.
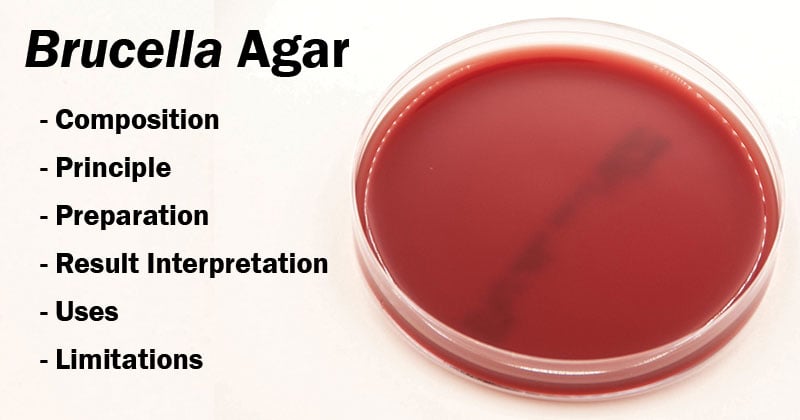
Result Interpretation on Brucella Agar
After incubation, most plates will show an area of confluent growth. Because the streaking procedure is, in effect, a “dilution” technique, diminishing numbers of microorganisms are deposited on the streaked areas. Consequently, one or more of these areas should exhibit isolated colonies of the organisms contained in the specimen. Further, the growth of each organism may be semi-quantitatively scored on the basis of growth in each of the streaked areas.
| Organisms | Growth |
| Brucella melitensis | Luxuriant, transparent, raised, convex, with an entire edge and a smooth, shiny surface. |
| Brucella ovis | Good, convex colonies |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | Good |
| Brucella suis | Luxuriant, transparent, raised, convex, with an entire edge and a smooth, shiny surface. |
| Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus | Inhibited |
| Escherichia coli | Inhibited |
Uses of Brucella Agar
- is used for the cultivation of Brucella spp. and other fastidious microorganisms in a laboratory setting.
- It is a general purpose medium for the cultivation of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus viridans, and Neisseria meningitidis.
- With the addition of blood, Brucella Agar is used to determine bacterial hemolytic reactions.
- It can be used as a base for the isolation of Campylobacter
- It is also recommended by APHA for isolation of Brucella species from foods.
- With the addition of 5% horse blood, the medium is used in qualitative procedures for the isolation and cultivation of non-fastidious and fastidious microorganisms from a variety of clinical and nonclinical specimens.
Limitations of Brucella Agar
- They are not intended for use in the diagnosis of disease or other conditions in humans.
- Due to nutritional variation, some strains may be encountered that grow poorly or fail to grow on this medium.
- All presumptive anaerobic organisms must be identified by the confirmatory test.
References
- https://foodsafety.neogen.com/pdf/acumedia_pi/7120_pi.pdf
- http://himedialabs.com/TD/M074.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/immunology-and-microbiology/brucella-agar
- http://bvascientific.com/Customer/miscne/specpages/211086.pdf
- https://www.thomassci.com/Laboratory-Supplies/Microbiological-Media/_/Brucella-Agar-Base
- Moyer N. P., and Holcomb L. A., Laboratory Diagnosis and Infectious Diseases: Principles and Practice, Vol. I, Springer-Verlag, New York
- http://www.oxoid.com/UK/blue/prod_detail/prod_detail.asp?pr=CM0169&c=UK&lang=EN
- https://www.health.ny.gov/guidance/oph/wadsworth/brucella_species.pdf
- http://microbiology.sbmu.ac.ir/uploads/Brucella.pdf

Good information about brucella media thanks