Coliforms refer to all aerobic and facultative anaerobic, gram-negative, non-spore-forming rod-shaped bacteria that ferment lactose with gas and acid formation within 48 hours at 35°C. Procedures to detect, enumerate, and presumptively identify coliforms are used in testing foods and dairy products. One method for performing the presumptive test for coliforms uses Violet Red Bile Agar (VRBA). Violet Red Bile Agar (VRBA) is a selective medium used to detect and enumerate lactose-fermenting coliform microorganisms.
Interesting Science Videos
Composition of Violet Red Bile Agar (VRBA)
| Ingredients | Gms/liter |
| Peptic digest of animal tissue | 7.000 |
| Yeast extract | 3.000 |
| Sodium chloride | 5.000 |
| Bile salts mixture | 1.500 |
| Lactose | 10.00 |
| Neutral red | 0.030 |
| Crystal violet | 0.002 |
| Agar | 15.00 |
Final pH (at 25°C): 7.4±0.2
Principle of Violet Red Bile Agar (VRBA)
- It relies on the use of the selective inhibitory components crystal violet and bile salts and the indicator system lactose and neutral red.
- Crystal violet and bile salts inhibit growth primarily of the Gram-positive accompanying bacterial flora.
- Degradation of lactose to acid is indicated by the pH indicator neutral red, which changes its color to red, and by precipitation of bile acids.
- Thus, the growth of many unwanted organisms is suppressed, while tentative identification of sought bacteria can be made.
- Organisms that rapidly attack lactose produce purple colonies surrounded by purple haloes. Non-fermenters or late lactose fermenters produce pale colonies with greenish zones.
Red, surrounded by reddish precipitation zones, diameter 1-2 mm: Lactose-positive Enterobacteriaceae: coliform bacteria, E. coli.
Pink pin-point colonies: Enterococci, possibly Klebsiella.
Colorless: Lactose-negative Enterobacteriaceae
- Peptic digest of animal tissue and yeast extract serve as sources of carbon, nitrogen, vitamins and other essential growth nutrients.
- Lactose is the fermentable carbohydrate, utilization of which leads to the production of acids.
- Neutral red indicator detects the acidity so formed.
- Crystal violet and bile salts mixture help to inhibit the accompanying gram-positive and unrelated flora. Sodium chloride maintains the osmotic equilibrium.
Preparation and Method of Use of VRBA
- Suspend 41.53 grams in 1000 ml distilled water.
- Heat with stirring to boiling to dissolve the medium completely.
Note: DO NOT AUTOCLAVE. - Cool to 45°C and pour into sterile Petri plates containing the inoculum.
- Transfer a 1 mL aliquot of the test sample to a petri dish.
- Add 10 mL of Violet Red Bile Agar (at 48°C) and swirl to mix.
- Allow medium to solidify before incubating at 35°C for 18 – 24 hours; use 32°C for dairy products.
- Examine for purple-red colonies, 0.5 mm in diameter (or larger), surrounded by a zone of precipitated bile acids.
- Continue with confirmatory testing of typical organism’s colonies.
Result Interpretation on Violet Red Bile Agar (VRBA)
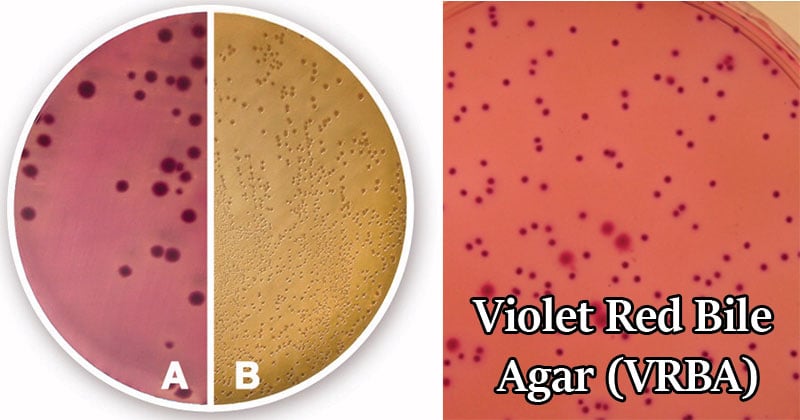
Image Source: LABM and Carl Roth
| Organisms | Growth |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | Mucoid, pink to pinkish-red |
| Escherichia coli | Pinkish red with bile precipitate |
| Salmonella Enteritidis | Colorless to orangish-yellow |
| Salmonella typhimurium | Fair to good growth; colorless colonies |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Partial to complete inhibition |
Uses of Violet Red Bile Agar (VRBA)
- VRBA is used for the isolation, detection, and enumeration of coli-aerogenes bacteria in water, milk, and other dairy food products and also from clinical samples.
Limitations of Violet Red Bile Agar (VRBA)
- Violet Red Bile Agar is not completely specific for enterics; other accompanying bacteria may give the same reaction.
- Due to varying nutritional requirements, some strains may be encountered that grow poorly or fail to grow on this medium.
- VRBA may not be completely inhibitory to Gram-positive organisms and will grow Gram-negative bacilli other than members of Enterobacteriaceae. Perform a Gram stain and biochemical tests to identify isolates.
- Boiling the medium for longer than 2 minutes can decrease the ability to support growth.
- It is recommended that biochemical, immunological, molecular, or mass spectrometry testing be performed on colonies from pure culture for complete identification.
- Enterococci may grow, and if so, usually appear pinpoint in size and rose-colored.
- Violet Red Bile Agar is not intended for use in the diagnosis of a disease or other conditions in humans.
References
- http://www.himedialabs.com/TD/M049.pdf
- http://www.labm.com/products/violet-red-bile-agar-vrba.asp
- https://catalog.hardydiagnostics.com/cp_prod/Content/hugo/VioletRedBileAgar.htm
- https://www.fda.gov/Food/FoodScienceResearch/LaboratoryMethods/ucm062976.htm
- https://foodsafety.neogen.com/pdf/acumedia_pi/7165_pi.pdf
- https://www.humeau.com/media/blfa_files/TC_211695-Violet-Red-Bile-Agar_EN_110909.pdf

Dr. Sir , 1/3 dilution of the sample of milk,after incubation about how many colony will be formation on vrba agar on.