Nitrogen Cycle: Steps, Process, Significance, Human Influence
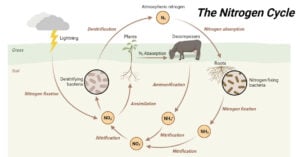
The movement of nitrogen between the atmosphere, biosphere, and geosphere in different forms is called the nitrogen cycle and is one of the major biogeochemical cycles. Importance of Nitrogen in Ecosystems Nitrogen is vital for maintaining … Read more