pBR322 is a commonly used cloning vector in E. coli and has tremendous applications in cloning.
pBR322 full form
p = plasmid
BR = Bolivar, and Rodriguez
322 = numerical designation
- It was constructed in 1977 in the lab of Herbert Boyer at The University of California in San Francisco.
- It is a synthetic plasmid and was the first artificial plasmid to be constructed and used as a cloning vector.
- pBR322 is one of the most studied plasmids.
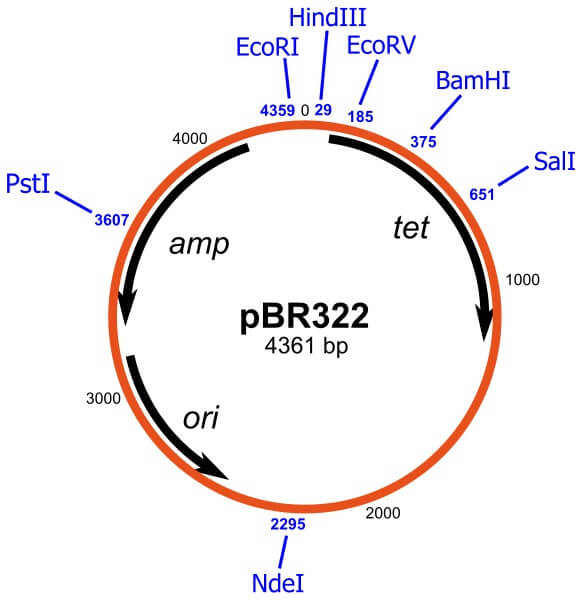
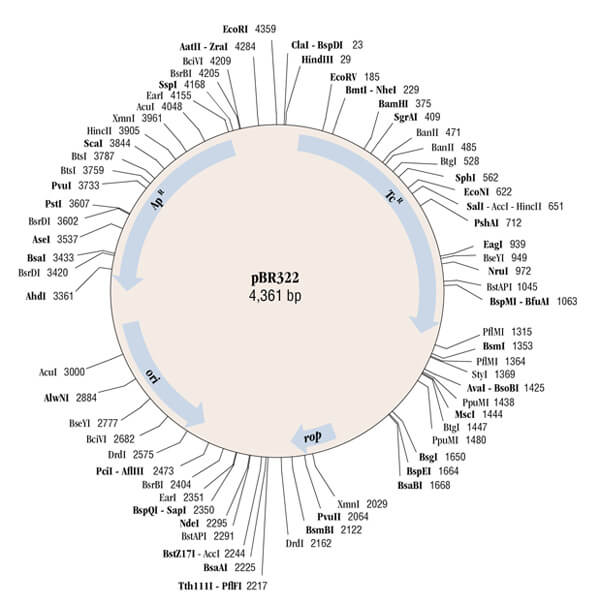
- It is 4362 base pairs long.
- It is completely sequenced, which means the whole sequence of pBR322 is known and studied.
- Its molecular weight is 2.83 x 106 Daltons.
Interesting Science Videos
Structure of pBR322
- Origin of replication
- Restriction enzyme sites
- Selectable marker sites
Origin of replication
- The origin of replication in plasmid pBR322 is known as pMB1.
- The copy number of this plasmid is 15-20.
Restriction enzyme sites
- Around 40 different restriction sites are present on the genome of pBR322.
- Almost 11 different restriction sites are present in the region of tetracycline resistance region.
- In the ampicillin resistance region 9 restriction sites of different enzymes are present.
- Some of the known restriction enzyme sites are – BamHI, HindIII, EcoRI, SaII, and many more.
Selectable marker sites
Two selectable marker sites or antibiotic resistance genes are present on the genome of this plasmid.
- Ampicillin resistance site – the ampicillin gene codes for β-lactamase, which can be used for screening microorganisms when a foreign DNA is being inserted in the plasmid.
- Tetracycline resistance site – this gene degrades the antibiotic tetracycline and can be used for screening microorganisms.
- These antibiotic resistance genes are useful in screening organisms after cloning.
Screening of recombinants containing pBR322
- Consider that the restriction enzyme BamHI is used to cut the plasmid at that specific position.
- BamHI lies in the tetracycline resistance region of plasmid pBR322.
- Now, the recombinant molecule of pBR322, which includes the newly inserted DNA molecule, will be sensitive to Tetracycline.
- But this recombinant molecule is resistant to Ampicillin, as the ampicillin resistance gene is fully functional.
- Hence, when the recombinant cells are plated on the medium containing ampicillin and incubated.
- The colonies that appear on plates containing a medium with ampicillin are transformed colonies containing cells with the newly inserted DNA molecule.
- The replica plate technique is used to confirm the transformed colonies.
- To confirm that the colonies on the ampicillin-containing media are transformed colonies, they are plated on the plates containing a medium inclusive of tetracycline.
- The colonies that do not grow on the medium inclusive of tetracycline are transformed colonies as the transformed colonies are sensitive to tetracycline.
Advantages of pBR322
- Due to its manageable size, plasmid pBR322 is widely used as a cloning vector.
- The presence of two antibiotic resistance genes eases the selection process of recombinants.
- Multiple restriction enzyme sites make the plasmid compatible in many ways.
- It has a high copy number which is highly favorable in genetic engineering.
Disadvantages
- Detection of recombinant cells having the newly inserted DNA molecule is time-consuming.
References
- Balbás, P., Soberón, X., Merino, E., Zurita, M., Lomeli, H., Valle, F., Flores, N., & Bolivar, F. (1986). Plasmid vector pBR322 and its special-purpose derivatives–a review. Gene, 50(1-3), 3–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(86)90307-0
- PRINCIPLES OF GENE MANUPULATION AND GENOMICS BY PRIMROSE AND TWYMAN
- http://vidyamandira.ac.in/pdfs/e_learning/ds_microbio/PLASMID%20CLONING%20VECTORS%20%20MCBA%20P7%20T.pdf
