Archaea vs Bacteria- Definition, 15 Major Differences, Examples
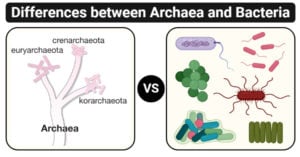
Image Source: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Created using biorender.com. Archaea Definition Archaea is a group of primitive prokaryotes that based on their distinct characteristics form a separate domain from bacteria and … Read more