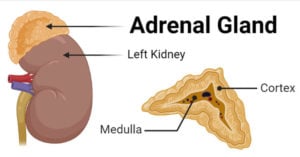
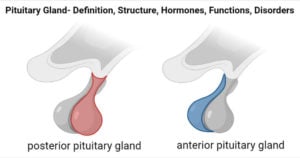
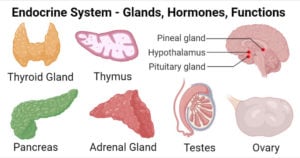
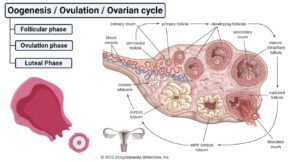
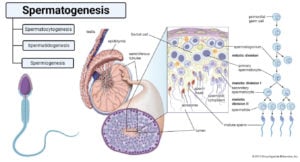
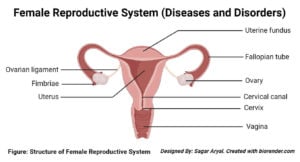
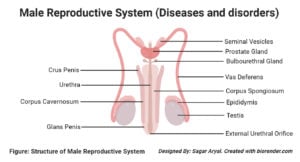
Adrenal Gland- Structure, Hormones, Functions, Disorders
The adrenal glands, also called suprarenal glands, are a pair of glands occurring on the top of kidneys and produce different steroid hormones. Structure of Adrenal Gland There are two … Read more