Introduction
Diseases and disorders of the male reproductive system include different diseases, infection,s and dysfunction in various organs in the male reproductive system. It can range from mild inflammation to reduced fertility in men. Most of the disorders in the male reproductive system are associated with the fluctuation of the sex hormone testosterone. In addition to this, however, other risk factors like age, family history, lifestyle, and consumption of different drugs are also associated with such disorders.
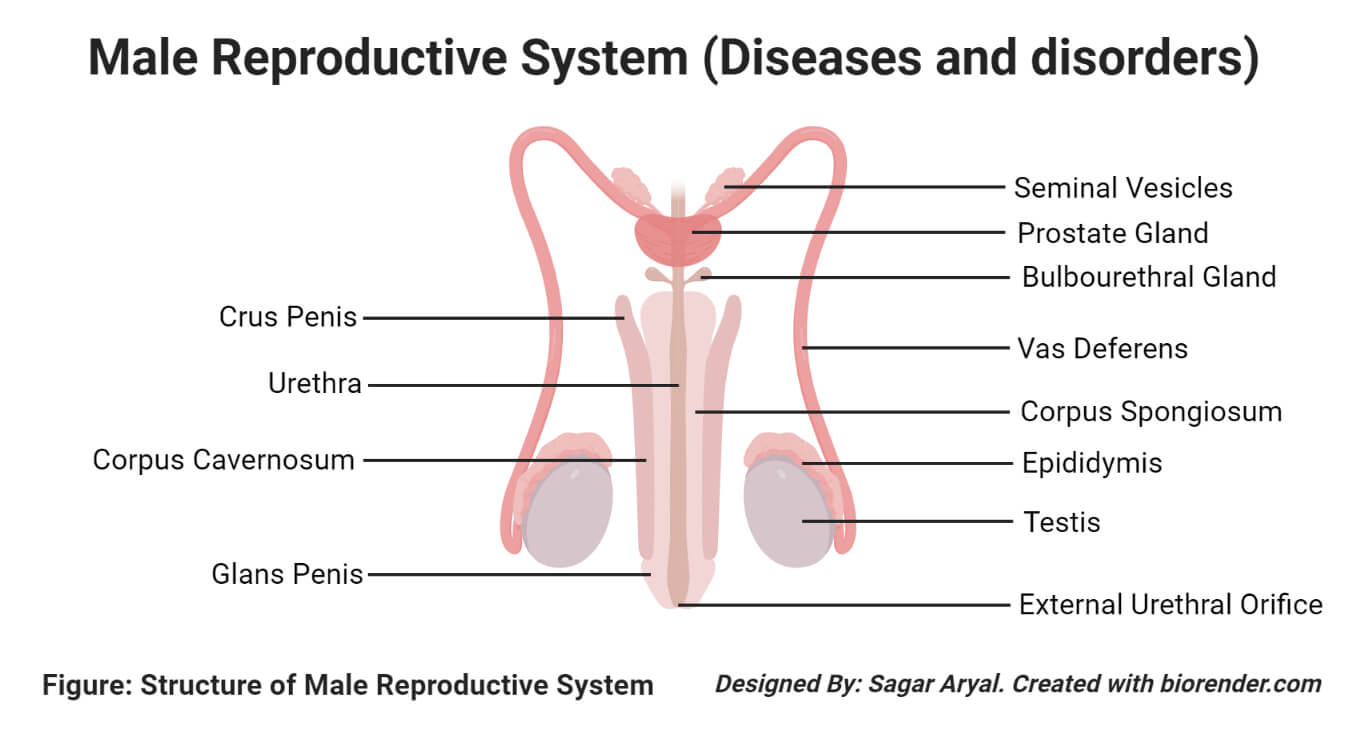
Different diseases and disorder associated with the male reproductive system are explained with respect to their organs as follows:
Interesting Science Videos
Penis
Infection of penis
- The inflammation of the glans and prepuce is often related to poor personal hygiene.
- In case of non-specific infection, also called balanitis, there is a high chance of the infection becoming chronic which might lead to fibrosis of the skin around the penis.
Erectile dysfunction
- Erectile dysfunction is a sexual disorder in a mature, sexually active male to develop or maintain an erection. It is found that this disorder occurs in 40% of males, occasionally.
- An erection in men is achieved when the columns of spongy muscles in the penis become engorged with blood so anything that hampers the flow of blood to these muscles can be a cause of this dysfunction.
- Besides, different surgical procedures might remove necessary structures required to develop an erection like the blood supply or the nerves.
- Erectile dysfunction is often associated with the treatment of prostate cancer, even though the prostate gland is not necessary for an erection.
- In many cases, the cause of erectile dysfunction is lower self-esteem and anxiety related to sex.
- Erectile dysfunction in men often results in psychological trauma in the man and his partners. Many cases of ED are not reported due to embarrassment among men.
Urethra Infection
- Gonococcal urethritis is a common specific infection of the urethra. Non-specific infection from the bladder (cystitis) and during surgery is also possible.
- Both of these infections spread out to other organs like epididymis, prostate, seminal vesicles, and testes.
- If the infection becomes chronic, it causes fibrosis in the urethra, which obstructs the urethra resulting in the retention of urine.
Epididymis and Testes Infection
- Infections in the epididymis and the testes occur through the spread of infection from the urethra. The microbes either pass through the vas deferens or lymph.
- Specific epididymitis occurs through the spread of gonorrhea from the urethra.
- Orchitis or testicular infection occurs due to the mumps virus originating from the parotid gland. Oedema is seen following the parotid swelling, and if the infection becomes bilateral, it might affect the seminiferous tubules and lead to sterility.
Undescended testis (cryptorchidism)
- In the embryonic stage, the testes are present in the abdominal cavity, and they drop to the scrotal sac by birth. However, if this process fails to happen and the condition is not corrected, it leads to infertility and an increased risk of testicular cancer.
Hydrocele
- A hydrocele is a fluid-filled space in the testes that leads to swelling. It is a common type of scrotal swelling and might be acute and painful or chronic.
- It causes discomfort and pain in the scrotal region.
- It might arise in the testes or might be secondary due to other infections or disorders.
Testicular tumors
- Testicular tumors mostly occur in children and young men and are the most prevalent malignancies in young men. Most of these are malignant and might spread to other organs and regions.
- Most of the tumors result due to cryptorchidism where the testes do not descend to the scrotal sac at the time of birth.
- Testicular tumors are characterized by the formation of lumps in the testes, which are mostly painless. These lumps result in a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum and might spread to other organs through lymph or blood.
Prostate gland Infection
- Acute prostatitis is a non-specific infection that usually occurs when the infection in other parts spreads to the prostate gland after cystoscopy or surgery where a part of the gland is removed.
- In the case of chronic infection, fibrosis of the gland occurs which might lead to obstruction of the urethra.
Benign prostatic enlargement
- Nodules appear in the prostate which causes swelling of the prostate gland. This swelling, in turn, obstructs the passage of urine and causes retention of urine in the bladder.
- This retention causes infection f the bladder, which might spread to other regions and cause other complications.
- Prostate enlargement is commonly associated with older men and is seen in 70% of men aged above 70. The specific cause is not known, but it is assumed to be associated with the acceleration of the aging process and decline in androgen secretion.
Malignant prostatic tumors
- Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men and is also the second leading cause of cancer deaths in men.
- Prostate cancer occurs when the glandular cells mutate into tumor cells. The cause is not yet known, but the androgen-estrogen imbalance may be significant, or viruses may be involved.
- If undetected, these tumor cells might affect the nearby organs like the seminal vesicles, or they might metastasize and travel in the bloodstream to other parts of the body.
- Most commonly, the metastases reach the bones and lymph nodes among other organs. Lumbar vertebrae are a common site for metastases.
- Prostate tumors affect the flow of urine in the urethra, leading to frequent urination, painful urination, and blood in the urine.
References and Sources
- Waugh A and Grant A. (2004) Anatomy and Physiology. Ninth Edition. Churchill Livingstone.
- Marieb EN and Hoehn K. (2013) Human Anatomy and Physiology. Ninth Edition. Pearson Education, Inc.
- https://www.ck12.org/book/ck-12-human-biology/section/20.5/
- https://www.dmu.edu/medterms/male-reproductive-system/male-reproductive-system-diseases/
- 1% – https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/CRC/PDF/Public/6072.00.pdf
- 1% – https://www.cancer.gov/types/metastatic-cancer
- 1% – https://veteriankey.com/testes-and-scrotum/
- 1% – https://pmj.bmj.com/content/78/924/590
- 1% – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9117-male-reproductive-system
- 1% – https://healthhearty.com/causes-of-prostate-infection
- 1% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Erectile_dysfunctions
- 1% – https://clinicalgate.com/diseases-of-the-male-reproductive-system/
- <1% – https://www.webmd.com/prostate-cancer/guide/impotence-prostate-cancer
- <1% – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S235262111500008X
- <1% – https://www.cancer.gov/types/testicular/patient/child-testicular-treatment-pdq
- <1% – https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/prostate-tumors
- <1% – https://ada.com/conditions/cryptorchidism/
