Interesting Science Videos
Anaphase Definition
This is the phase that separates duplicate genetic materials that are carried in the nucleus of the parent cell, into the two identical daughter cells.
- In the previous phase, metaphase, the sister chromatids (replicated chromosomes) are aligned along the cell’s equator on the metaphase plate.
- Therefore, during anaphase, each pair of chromosomes separates into two identical but independent chromosomes.
- Each of these chromosomes gets separated by mitotic spindles known as microtubules, attached to the chromosomes at both ends of the cell.
- Separation occurs simultaneously at the centromere and each separated chromosome gets pulled by the spindles to the opposite poles of the cell.
- The function of anaphase is to ensure that each daughter cell receives identical sets of chromosomes before the final phase of the cell cycle, which is telophase.
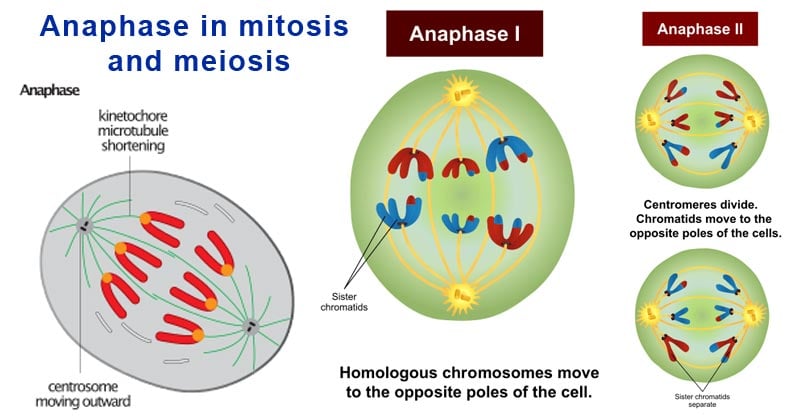
Image Source: Wikipedia and Wikipedia (Ali Zifan).
What happens during anaphase?
- Anaphase begins when the anaphase-promoting complex which terminates the metaphase.
- This anaphase-promoting complex tags securin, a protein that helps in the transition from metaphase to anaphase and also used for the destruction of securin by incorporating ubiquitin hence acting as an inhibitory chaperone.
- Securin acts by inhibiting the separase enzyme, a type of protease. When securin is destroyed, the separase enzyme is released which then breaks down cohesin protein which holds the sister chromatids together.
- Several unique microtubules are involved in the creation of the forces required for the separation of chromatids. These include Astral microtubules, kinetochore microtubules, and the interpolar microtubules.
- This leads to the splitting of the centromere, pulling the sister chromatids to the poles of the cell by the kinetochore microtubules.
- The separated sister chromatids then form a V or Y-shape at either pole of the cell.
- The astral and interpolar microtubules contribute to the stretching and shaping of the cell which takes up an oval shape.
- Separation of the chromatids into single sister chromosomes means that they contain the same genetic information but function independently as new cells.
- Successful completion of anaphase leads to the next phase of the cell cycle which is telophase.
Anaphase in mitosis
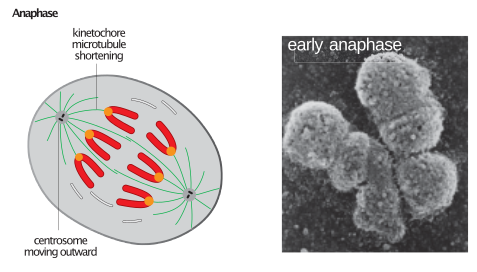
Figure: Anaphase in Mitosis. Image Source: Wikipedia
- Anaphase in mitosis is triggered by the separation of the sister chromatids with the help of separase.
- Separase breaks the cohesion that binds the sister chromatids, as the microtubules pull the sister chromatids towards the opposite plea of the cells.
- The astral and interpolar microtubules play a major role in lengthening and elongating the cell which takes an oval shape.
Anaphase in meiosis
- The anaphase of meiosis is made up of two consecutive cell divisions, i.e anaphase I and anaphase II.
- In this stage of meiosis, since there is no DNA replication in between, the diploid cell with two alleles for each gene gets reduced to a haploid cell containing a single allele at each gene.
- Generally, anaphase I involve separating the chromosomes from each sister chromatid to the opposite poles still attached to the microtubules of the cell while anaphase 2 involves the actual split of the sister chromatids into single chromatids.
Anaphase I
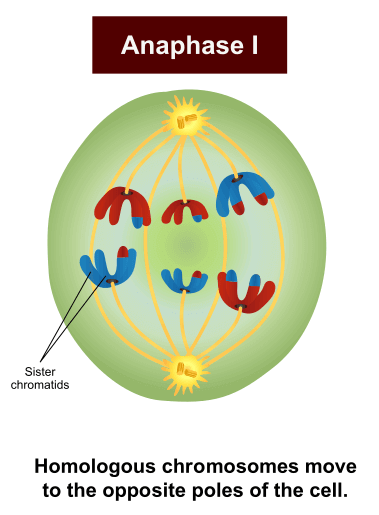
Figure: Anaphase I in Meiosis. Image Source: Wikipedia (Ali Zifan).
- During this phase, the kinetochore microtubules shorten thus pulling the homologous chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell.
- The non-kinetochore microtubules start to lengthen thus pushing the centrosomes apart.
- The cell also elongates as it prepares for dividing at the center.
- The cohesins around the centromere remain protected by a protein known as Shugoshin (guardian spirit), preventing the sister chromatids from separating while the homologs are segregated.
Anaphase II
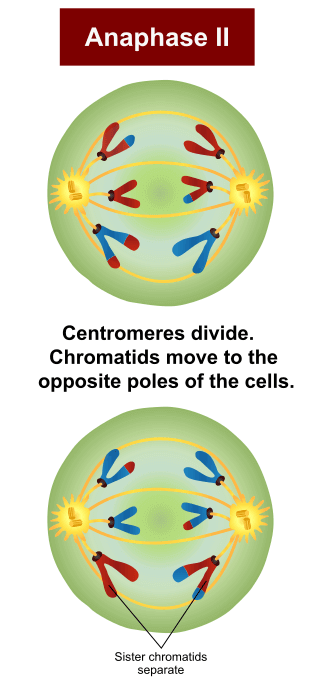
Figure: Anaphase II in Meiosis. Image Source: Wikipedia (Ali Zifan).
- This is the phase after metaphase 2 whereby the remaining centromeric cohesins which are not protected by the Shugoshin anymore are cleaved.
- This allows the separation of the sister chromatids which are then singly referred to as sister chromosomes. They move towards the opposite poles of the cells.
Video Animation: What happens in anaphase? (Video By: MooMooMath and Science)
Reference and Sources
- https://www.expii.com/t/anaphase-definition-diagrams-10161
- Lumenlearning.com/Biology For Major
- https://teaching.ncl.ac.uk/bms/wiki/index.php/Anaphase
- https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/anaphase-179/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Meiosis#Anaphase_I
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anaphase
- https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/cellular-molecular-biology/mitosis/a/phases-of-mitosis
- http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/mitosisisg/anaphase.html

