Optochin, also called ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride, is a derivative of quinine, an antimalarial agent. It was introduced by Morgenroth and Levy in 1911 as an antibiotic for treating pneumococci infection (infection of Streptococcus pneumoniae). Although optochin can inhibit or kill S. pneumoniae, it is not used as a treatment measure; instead, it is used in the differentiation of S. pneumoniae among other α-hemolytic Streptococci (viridans Streptococci).
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Gram-positive, catalase-negative, α-hemolytic, anaerobic but aerotolerant, diplococcus of genus Streptococcus of the family Streptococcaceae in the class Bacilli. It is commonly found in the upper human respiratory tract, but in immunocompromised and susceptible patients it leads to pneumoniae, meningitis, otitis media, arthritis, and many other infections. As it is a major cause of pneumonia, it is called ‘pneumococcus.’
S. pneumoniae is typically found in the respiratory tract and isolated from respiratory samples where other diverse groups of α-hemolytic Streptococci are also found. Hence, it is difficult to identify S. pneumoniae. Fortunately, Bowen and Jeff in 1955 impregnated a disk with optochin and proposed to use it as a method to differentiate S. pneumoniae from other viridans Streptococci. This method is termed an optochin susceptibility test to identify the pneumococcus bacteria.
Interesting Science Videos
Objectives
- To differentiate S. pneumoniae from other α-hemolytic (viridans) Streptococci
Principle
α-hemolytic Streptococci produce colonies with the green-colored zone of incomplete hemolysis in a blood agar medium. So, it is difficult to identify S. pneumoniae among other viridans Streptococci based on hemolysis and other common biochemical characteristics.
S. pneumoniae is the only known optochin-sensitive viridans Streptococcus. Hence, S. pneumoniae shows a clear zone of inhibition around the optochin-impregnated disk; whereas other viridans Streptococci do not display a zone of inhibition around the optochin-impregnated disk. Based on this feature, S. pneumoniae can be easily differentiated from other viridans Streptococci.
Requirements
Culture Media
A 5% Sheep Blood Agar Plate is used as culture media to perform the optochin sensitivity test. This media is prepared by adding 5% v/v defibrinated sheep blood in a molten blood agar base medium.
Composition of Blood Agar Base
Beef Heart Peptone- 10.0 grams (Alternatively, Meat Extracts- 10.0 grams)
Peptone- 10.0 grams (Alternatively, Tryptose- 10.0 grams)
Sodium Chloride- 5.0 grams
Agar- 15.0 grams
Final pH 7.3 ±0.2 at 25°C
Preparation of BA Plate (BAP)
- Measure the appropriate amount of blood agar base powder (or the media components) and mix in the water of the required volume in a conical flask (or glass bottle) according to the instruction of the manufacturing company.
- Stir well using a magnetic stirrer or manually and heat to boiling so that all the components and agar dissolve completely in water.
- Autoclave the flask or bottle at 121°C and 15 lbs pressure for 15 minutes and let it cool to around 40 – 45°C.
- Pour 5% (5 to 10%) v/v sterile defibrinated Sheep Blood into the flask with blood agar base slowly with constant stirring. Mix properly so that blood dissolves uniformly in the medium. This mixture is the Blood Agar.
- In a sterile Petri plate (glass plate with 10 cm diameter), pour around 25 mL of the blood agar and let it solidify properly by leaving it at room temperature. (Store BAPs in a freeze at 4°C for use up to 2 to 4 weeks maximum)
Reagents
Optochin-impregnated disk (6mm disk with 5μg of optochin)
Defibrinated Sheep Blood (for BAP preparation)
McFarland Standard number 0.5
Composition
1% anhydrous barium chloride (BaCl2) solution
1% sulfuric acid (H2SO4) solution
Preparation of number 0.5 McFarland Standard Suspension
- In a clean and clear test tube, add 9.95 mL of 1% H2SO4 and 0.05 mL of 1% BaCl2 solution
Equipment
| Petri Plates Forceps | Weighing Machine Autoclave | Bunsen burner CO2 Incubator | Inoculating loop/(Cotton Swab) PPE Other laboratory materials |
Test organism (sample bacteria)
Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 49619 – Positive control
Streptococcus mitis ATCC 49456 or Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 or Streptococcus pyogenes ATCC 12384 – Negative control
Procedure
- In a sterile test tube, prepare a bacterial suspension of well isolated α-hemolytic colonies of the sample organism. Adjust the turbidity of the suspension to 0.5 McFarland standards.
- Using a sterile inoculating loop or cotton swab, streak (or spread) the bacterial suspension in two directions (at least) over the 5% Sheep Blood Agar Plate.
(While using the known culture of S. pneumoniae for any purpose other than identification, MHA can be used.)
- Let the suspension to adhere the plate and dry leaving the plate in an upright position for about 5 to 10 minutes.
- Using sterile forceps, place an optochin antibiotic disk in the area of inoculation and gently press the antibiotic disk to ensure its adherence.
- Incubate anaerobically (in 5 to 10% CO2 environment) at 35±2°C for overnight (18 to 24 hours).
- Following the incubation period, observe the formation of a zone of inhibition around the optochin antibiotic disk and measure the zone diameter.
Result and Interpretation
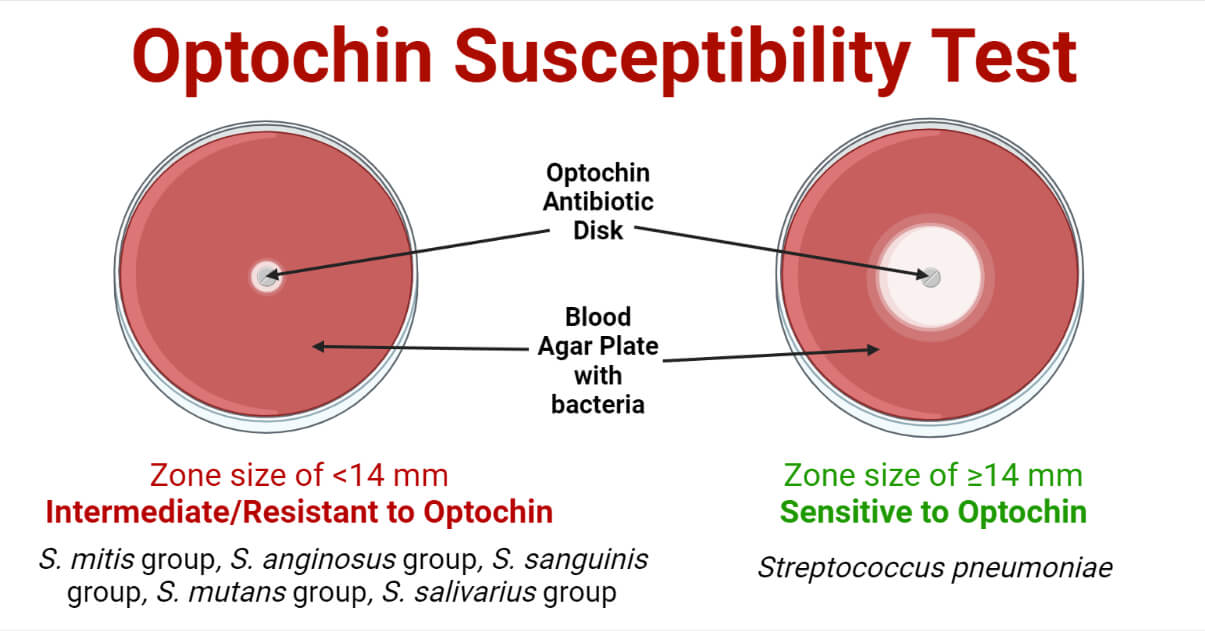
Zone size ≥14 mm = Optochin Sensitive
Zone size <14 mm = Optochin Intermediate
No zone of inhibition = Optochin Resistant
- If the bacteria is Gram-positive cocci in pair, catalase-negative, and α-hemolytic and optochin sensitive report, it as Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- If the bacteria are Gram-positive cocci in pair, catalase-negative, and α-hemolytic and optochin intermediate, perform the spot bile solubility test. If the bacteria is bile soluble, report it as Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- If the bacteria are Gram-positive cocci, and α-hemolytic and optochin resistant report it as Viridans Streptococci.
Optochin Susceptible Bacteria
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Optochin Resistant Bacteria
S. mitis group, S. anginosus group, S. sanguinis group, S. mutans group, S. salivarius group
Quality Control
Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 49619 produces a well-defined zone of inhibition of ≥14 mm around the optochin disk.
Streptococcus mitis ATCC 49456 or Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 produce no zone of inhibition around the optochin disk.
Precautions
- Don’t pour blood in molten blood agar base if it is above 45°C.
- Pour the media into petri plates in a sterile zone before the temperature of the molten media drops below 40°C; otherwise, clumps may form.
- For bacterial identification, always use 5% sheep blood agar.
- Place the disk about 25 mm away from the edge of the plate. If using multiple antibiotic disks, place the disk at least 25 mm apart from each other.
Applications
- Used for identification of (differentiation of) Streptococcus pneumoniae from other viridans Streptococci.
Limitations
- Need bile solubility test if the test bacteria are α-hemolytic but show intermediate susceptibility to the optochin.
- Occasionally, S. pneumoniae resistant to optochin has been reported.
- Require 5% sheep blood agar medium and CO2 incubator for culture and incubation.
- Optochin-resistant/intermediate colonies may or may not be S. pneumoniae so need verification.
- It is a culture-based method so requires at least 24 hours for results and interpretation.
References
- Leber, Amy L., editor in chief. (2016). Clinical microbiology procedures handbook (Fourth edition). Washington, DC : ASM Press 1752 N St., N.W., [2016]
- Tille, P. M., & Forbes, B. A. (2014). Bailey & Scott’s diagnostic microbiology (Thirteenth edition.). St. Louis, Missouri: Elsevier.
- BOWEN MK, THIELE LC, STEARMAN BD, SCHAUB IG. The Optochin sensitivity test: a reliable method for identification of pneumococci. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Apr;49(4):641-2. PMID: 13406403.
- Ethylhydrocupreine (Optochin) | Antimicrobial Agent | MedChemExpress
- Optochin – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- Optochin senstivity test principle-procedure (medicallabtechnology.com)
- Optochin Susceptibility Test: Principle, Objective, Procedure And Results (microbiologynote.com)
- Optochin Susceptibility Test for the identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae (microbiologyinfo.com)
- Optochin Sensitivity Test: Principle, Procedure, Result and interpretation (universe84a.com)
- Optochin Test: Principle, Requirements, Procedure, Result Interpretation and Limitations – Online Science Notes
- Laboratory Methods for the Diagnosis of Meningitis – CHAPTER 8: Identification and Characterization of Streptococcus pneumoniae (cdc.gov)

I want to study Msc in school but you refuse to guide me and tell me the cost. I’m from Nigeria