LAP test is used for the differentiation and identification of catalase-negative Gram-positive cocci bacteria. Specifically, it is used to distinguish Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Pediococcus, and Lactococcus species from Aerococcus and Leuconostoc species.
Leucine aminopeptidases are metallopeptidases that hydrolyze leucine residues from the N-terminus of proteins or/and peptides. They are proteolytic enzymes in the peptidase family that help to metabolize proteins for bacterial survival as well as aid in bacterial pathogenesis. However, not all bacteria have the ability to synthesize leucine aminopeptidases (LAP). Hence, the detection of LAP production is an important technique to classify bacteria. LAP test is used as a biochemical test in the microbiology lab to classify bacteria as leucine aminopeptidase-producing and non-producing groups.
Interesting Science Videos
Objectives of LAP Test
- To assess the ability of bacteria to synthesize leucine aminopeptidases enzymes
- To differentiate and presumptively identify catalase-negative Gram-positive cocci bacteria
Principle of LAP Test
The leucine aminopeptidase enzymes synthesized by bacteria hydrolyze the leucine-p-naphthylamide components in the LAP disk. Hydrolysis of leucine-p-naphthylamide by LAP enzymes releases leucine and free β- naphthylamide. The free β- naphthylamide reacts with cinnamaldehyde reagent (N, N-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde) forming a bright pink or cherry red color Schiff base indicating a positive LAP test.
Requirements for LAP Test
Reagents
- LAP Disks (Disks impregnated with leucine-p-naphthylamide)
- LAP Reagent
0.01% p-N, N-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde is used as a LAP reagent. The PYR reagent and LAP reagent are the same.
Composition of LAP Reagent:
N, N-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde- 1.0 grams
Concentrated Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)- 10.0 mL
Distilled Water- 990.0 mL
(Reference: PYR Reagent (himedialabs.com))
Preparation of PYR Reagent:
- Add 1.0 grams of N, N-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde in 990.0 mL of distilled water and slowly add 10.0 mL of concentrated HCl with constant stirring.
- Mix properly so that N, N-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde dissolves completely.
- Store at 2 to 8°C in a dark place.
- Distilled water
Equipment
| Petri plates | Bunsen burner | Inoculating loop | Forceps |
PPE and other general laboratory materials
Test Organisms (Sample Bacteria)
Positive Control: Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212
Negative Control: Aerococcus viridans ATCC 11563
Procedure of LAP Test
- Place a LAP disk in a sterile petri plate with forceps.
- Moisten the disk with sterile distilled water.
- Using a sterile inoculating loop, pick up 1 or 2 loops full of well-isolated sample bacteria and rub them onto the LAP disk.
- Incubate the plate aerobically for 5 minutes at room temperature.
- Add 1 to 2 drops of LAP reagent over the seeded LAP disk.
- Observe for color change after 2 minutes of addition of the reagent.
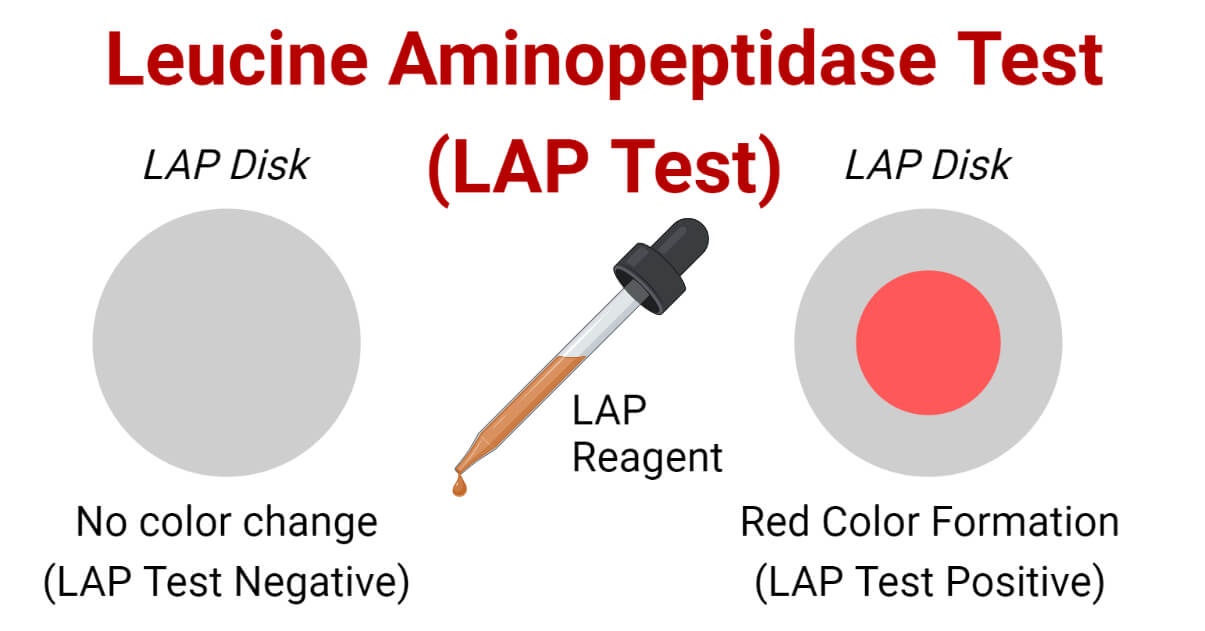
Result and Interpretation of LAP Test
- Development of bright pink or cherry red or reddish-purple color over disk after 2 minutes of addition of the LAP reagent indicates a positive reaction (LAP test positive).
- The development of pink color indicates a weak reaction and is considered positive.
- No color change or formation of yellow color, or orange color after the addition of the LAP reagent indicates a negative reaction (LAP test negative).
LAP Test Positive Bacteria
Streptococcus spp., Enterococcus spp., Lactococcus spp., and Pediococcus spp.
LAP Test Negative Bacteria
Leuconostoc spp., Aerococcus spp., Tetragenacoccus spp., etc. (Some Aerococcus spp. give variable results (Aerococcus urinae may give positive results))
Quality Control
Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 results in the formation of bright pink (red) color over the disk within 1-2 minutes of the addition of the LAP reagent.
Aerococcus viridans ATCC 11563 doesn’t form pink or red color (doesn’t change color) after the addition of the LAP reagent.
Precautions
- Store the LAP disk and reagent in cold and dark conditions.
- Don’t saturate the LAP disk with distilled water, just moisten it slightly.
- Transfer a heavy inoculum and rub it over the disk. The use of too little inoculum may give false negative results or may result in the formation of slight pink color.
Applications of LAP Test
- Definitive differentiation and identification of catalase-negative, Gram-positive cocci.
Limitations of LAP Test
- Application limited to catalase-negative, Gram-positive cocci bacteria only.
- Insufficient inoculum may give false negative results.
- Is not enough for the complete identification of bacteria; hence, requires other biochemical tests to confirm the identification of the sample bacteria.
References
- Leber, Amy L., editor in chief. (2016). Clinical microbiology procedures handbook (Fourth edition). Washington, DC : ASM Press 1752 N St., N.W., [2016]
- Tille, P. M., & Forbes, B. A. (2014). Bailey & Scott’s diagnostic microbiology (Thirteenth edition.). St. Louis, Missouri: Elsevier.
- Matsui M, Fowler JH, Walling LL. Leucine aminopeptidases: diversity in structure and function. Biol Chem. 2006 Dec;387(12):1535-44. doi: 10.1515/BC.2006.191. PMID: 17132098.
- Leucine Aminopeptidase (LAP) Test: Principle, Procedure, Results • Microbe Online
- Leucine Aminopeptidase (LAP) Test Principle, Procedure, Results (microbiologynote.com)
- Leucine amino peptidase (LAP) Test – Procedure, Uses and Interpretation (microbiologyinfo.com)
- Leucine Amino Peptidase (LAP) test – Online Biology Notes
- LAP (Leucine Aminopeptidase) Test » Clinical Laboratory Science (clinicalsci.info)

Well explained and understandable