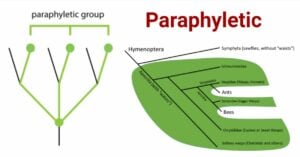
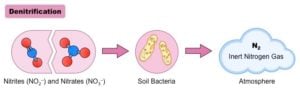
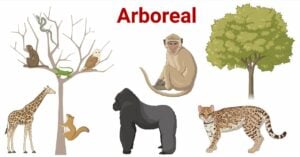
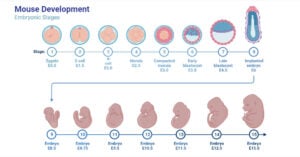
Gradualism: The Power of Incremental Change
Gradualism is a philosophical or conceptual approach emphasizing incremental change over time rather than sudden or abrupt transformations. It suggests that significant developments or transformations occur gradually through small, incremental … Read more