Theria: Characteristics, Diversity, Types, Examples
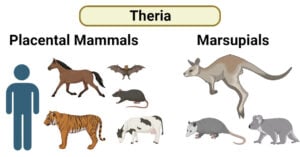
Theria is a subclass of mammals, including placental mammals (Eutheria) and marsupials (Metatheria). Placental mammals have a placenta, nourish their young internally, and include diverse groups like primates and rodents. … Read more