The body parts require blood to receive oxygen and perform metabolic processes. The blood is transported through closed vessels known as blood vessels.
The blood vessels have different sizes and functions. They are three types:
Interesting Science Videos
What are Arteries?
- The arteries are responsible for carrying the blood from the heart into the different body parts.
- The walls of arteries consist of three layers of tissue as follows:
- Tunica Externa: It is the outer layer that consists of fibrous tissue (collagen fibers).
- Tunica Media: It is the middle layer of the vein. It consists of smooth muscle and elastic tissue.
- Tunica Interna: It is the inner layer that forms the surface of the lumen. It comprises squamous epithelium, also known as endothelium.
What are Veins?
- The veins are responsible for carrying the blood from the different body parts toward the heart.
- The veins also comprise three layers i.e. tunica externa, media, and interna arranged in similar patterns as in veins from outer to inner portion respectively whereas the amount of tissues on the basis of width may vary in both veins and arteries.
What are Capillaries?
- They have very thin walls and form an extremely fine network of small tubes.
- They consist of just one layer of tissue called the endothelial layer.
- The endothelial layer is so thin and has higher permeability allowing the influx and efflux of chemicals in capillaries.
- They are also fenestrated, and hence diffusion of chemicals can occur through them.
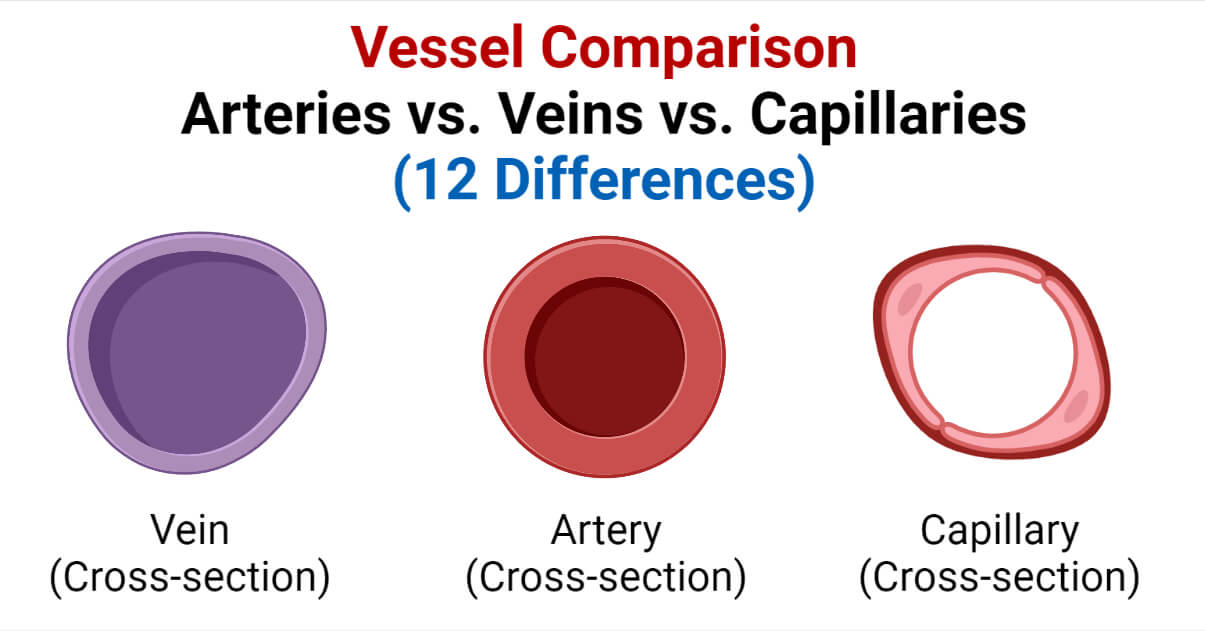
Main differences between the different types of blood vessels
| Arteries | Veins | Capillaries |
| It transfers blood from the heart to the tissues. | It transfers the blood from the different body parts into the heart. | It helps in the exchange of nutrients in the tissues. They also connect the veins and arteries. |
| The blood flows at higher pressure into the arteries. | Blood flows at a lower pressure than in arteries. | Blood flows at least pressure in this. |
| All arteries except one (i.e. pulmonary artery) carry pure or oxygenated blood. | All veins except one (pulmonary vein) carry impure or deoxygenated blood. | They connect the blood vessels to the cells. |
| They are deep-seated in the body. (Exception in wrist and neck part of our body) | They are present superficially. | They are located inside the tissues. |
| The wall is thick, more elastic, and non-collapsible. | The wall of the vein is thin, less elastic than arteries, and can be collapsible. | The walls are extremely thin in capillaries. |
| The lumen is narrow and hence the blood flows at a higher speed. | The lumen is wider than the artery. | The lumen is extremely narrow compared to veins and arteries i.e. around 7-10 micrometres in diameter. |
| There is the absence of valves. | It has the presence of valves that aid in the prevention of the backflow of blood. | No valves are present. |
| The three layers have the following features: – Tunica externa is less developed and lesser in strength. – Tunica media has more muscle. – Tunica media has more elongated endothelial cells. | The three layers have the following features: – Tunica externa is more developed and strong. – Tunica media has less muscle. – Tunica interna has less elongated endothelial cells. | There is only one thin layer i.e. tunica interna or endothelium. |
| May appear bright red in color. The color is provided by the flowing blood in them. | May appear dark red in color. | They can be bright red or dark red or purple as they carry every type of blood. |
| It is less distensible. | It is more distensible as the walls are thinner than the arteries. | More distensible due to thin walls. |
| It includes large arteries called the aorta and smaller ones called arterioles. | It includes larger veins called venacava (superior and inferior venacava) and smaller ones called venules. | |
| Around 15% of the blood resides in arteries. | Around 65% or more blood resides in the veins at any time. |
References
- Keshari A.K. and Ghimire K.R. 2010. Selective Reabsorption. A textbook of higher secondary biology. Vidyarthi publications. Kathmandu. Pg. 134-135.
- Accessed from: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21640-blood-vessels. Accessed on: 11/20/2022.
- Nicola S. (2021). Accessed from: https://www.webmd.com/heart/difference-between-arteries-veins-capillaries. Accessed on: 11/20/2022.
- Tucker WD, Arora Y, Mahajan K. Anatomy, Blood Vessels. [Updated 2022 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470401/
- Abramson D.I. (1962) Blood Vessels and Lymphatics. 1st ed. Elsevier.
