Casein Hydrolysis Test is the biochemical test used to determine the ability of bacteria to synthesize caseinase enzyme.
Casein is the major protein (phosphoprotein) with a molecular formula of C81H125N22O39P, found in milk. It is also known as the ‘milk protein’. Some bacteria have the capacity to produce a proteolytic exoenzyme caseinase showing casein hydrolyzing activity. Caseinase hydrolyzes the casein into smaller soluble amino acid units. But not all bacteria are able to synthesize this enzyme and hence, only some species can hydrolyze the casein. Based on this property, a test was devised to classify bacteria and identify them phenotypically, called the casein hydrolysis test.
This test is mostly done on microorganisms that are of concern to or isolated from food, especially milk and dairy products.
Interesting Science Videos
Objectives of Casein Hydrolysis Test
- To determine the ability of bacteria to synthesize caseinase enzyme.
- To determine the ability of the organism to degrade the casein protein.
Principle of Casein Hydrolysis Test
The medium (SM medium or Casein medium) contains casein proteins which are white-colored, insoluble protein and makes the medium opaque and milky white. Being a large macromolecule, bacteria can’t utilize the casein molecules directly for metabolism. So, bacteria produce caseinase, a proteolytic enzyme capable of hydrolyzing casein into smaller amino acids and peptides. This proteolysis will result in the formation of a clear transparent zone in the agar plate where casein has been hydrolyzed – indicating a positive result.
However, not all bacteria have the capacity to synthesize this extracellular proteolytic enzyme, caseinase. Therefore, bacteria can be differentiated based on their ability to produce caseinase enzymes.
Requirements for Casein Hydrolysis Test
a. Culture Media
Skim Milk (SM) Agar is used for the casein hydrolysis test. This medium contains a high concentration of casein in skim milk powder and is suitable for detecting casein hydrolysis.
Composition of Skim Milk Agar per 1000 mL
Skim Milk Powder (SM powder)- 28.00 grams
Yeast Extract- 2.50 grams
Tryptone- 5.00 grams
Glucose (Dextrose)- 1.00 grams
Agar- 15.00 grams
Final pH 7.0 ±0.2 at 25°C
(Reference: SM Agar (himedialabs.com))
Preparation of SM Agar
- Measure the appropriate amount of SM agar media powder (or the media components) and mix in the water of the required volume in a conical flask (or glass bottle) according to the instruction of the manufacturing company (51.50 grams per 1000 mL).
- Stir well using a magnetic stirrer or manually and heat to boiling so that all the components and agar dissolve completely in water.
- Autoclave the media at 121°C and 15 lbs pressure for 15 minutes.
- Let it cool to about 40 – 45°C and pour in a sterile petri plate (about 25 mL in a 10 cm diameter petri plate).
- Let the media solidify completely a room temperature.
b. Reagents
Although no additional reagents are required for the test, a 10% trichloroacetate solution can be used to make the zone more clearly visible.
c. Equipment
| Petri plates Incubator | Weighing Machine Autoclave | Bunsen burner | Inoculating loop |
PPE and other general laboratory materials
d. Test Organism (Sample Bacteria)
Positive Control: Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853
Negative Control: E. coli ATCC 25922
Procedure of Casein Hydrolysis Test
- Using a sterile inoculating loop, pick up a heavy inoculum from a well-isolated colony of fresh culture (18 to 24 hours old culture).
- Inoculate the sample organism plate by drawing either a straight line or a zig-zag line over the surface of the SM agar plate.
- Incubate the plates at 25 to 35±20C. Incubation at 25 to 300C requires prolonged incubation of up to 14 days before reporting negative. Incubation at 35±2°C can give results at about 24 hours.
(Incubate two sets of plates; one at 25±2°C and another at 35±2°C and read the result after a suitable incubation period.)
- Following incubation, observe the plate for the development of a clear zone of casein hydrolysis around the line of bacterial growth.
(For more clear display of the zone of hydrolysis, flood the plate with 10% trichloroacetate solution.)
Result and Interpretation of Casein Hydrolysis Test
- A positive test is indicated by the formation of a clear transparent zone of hydrolysis (casein hydrolysis) around the bacterial colony (in the line).
- A negative test is indicated by no clear zone of hydrolysis around the bacterial growth line (colonies).
Casein Hydrolyzing Bacteria
Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Lactococcus lactis, Streptomyces spp., Actinomadura spp.,
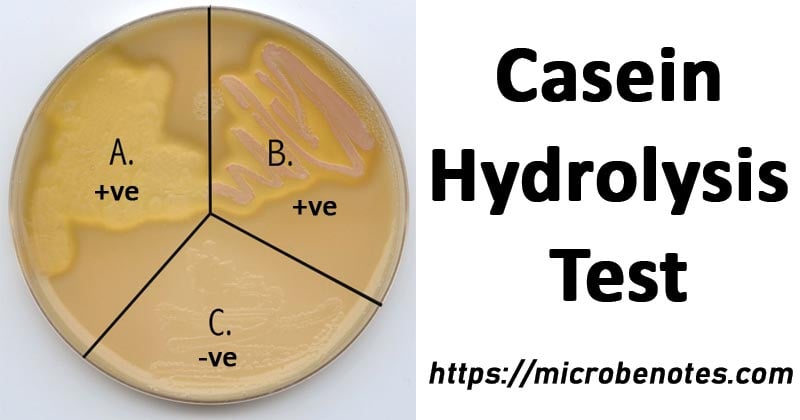
Quality Control
Inoculation of the SM agar with the above-mentioned control organisms and incubation at 35±2°C for 24 hours will show the following results. And, if the following results are obtained, we can be sure that the media and incubation conditions are accurate for the test.
- A clear transparent zone of hydrolysis is produced around the line of growth (colonies) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853.
- No zone of hydrolysis is produced around the line of growth (colonies) of E. coli ATCC 29522.
Precautions
- It is better to use heavy inoculum for bigger zone size and quick results.
- Be sure to incubate for at least 3 days at 35±20C and for at least 14 days at 250C before reporting negative. (Casein hydrolysis may be delayed in some organisms.)
Applications of Casein Hydrolysis Test
- Identification of bacteria isolated from milk and milk products.
- Differentiation of enteric bacteria, and members of Bacillaceae.
- Used in differentiation and identification of Actinomycetes.
Limitations of Casein Hydrolysis Test
- It is not a confirmatory test; hence, it requires other biochemical test results for the complete identification of the unknown bacteria.
- Require a longer incubation period.
- Fastidious organisms don’t grow in the medium and are difficult to test.
References
- Tille, P. M., & Forbes, B. A. (2014). Bailey & Scott’s diagnostic microbiology (Thirteenth edition.). St. Louis, Missouri: Elsevier.
- Aneja K.R. 2003. Experiments in Microbiology, Plant Pathology and Biotechnology, fourth revised edition, New Age International (P) limited, Ansari road, Daryaganj, New Delhi-110002.
- Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia. “casein”. Encyclopedia Britannica, 9 Feb. 2023, https://www.britannica.com/science/casein. Accessed 17 February 2023.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 73995022, Casein. Retrieved February 17, 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Casein.
- Casein Hydrolysis Test: Principle, Procedure, and Uses • Microbe Online
- 7.1: Introduction to Biochemical Tests Part I – Biology LibreTexts
- Casein Hydrolysis Test – Principle, Procedure, Uses and Interpretation (microbiologyinfo.com)
- 30: Casein Hydrolysis – Biology LibreTexts
- Casein Hydrolysis Test Principle, Procedure, Result (microbiologynote.com)
- Casein Hydrolysis (asm.org)
- Casein Hydrolysis Test: Result, Principle, and Procedure (researchtweet.com)
- Bacterial Identification Tests (unlv.edu)
- Casein Hydrolysis Test – As compounds catalyze every physiological response, detecting the catalyst – Studocu

Good information regarding casein hydrolysis test. It would have been more better if the hydrolysis of casein is represented by chemical reaction in principle of the test.